Progressive muscle metaboreflex activation gradually decreases spontaneous heart rate baroreflex sensitivity during dynamic exercise
- PMID: 19966049
- PMCID: PMC2822574
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00908.2009
Progressive muscle metaboreflex activation gradually decreases spontaneous heart rate baroreflex sensitivity during dynamic exercise
Abstract
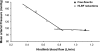
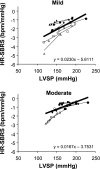
Ischemia of active skeletal muscle elicits a pressor response termed the muscle metaboreflex. We tested the hypothesis that in normal dogs during dynamic exercise, graded muscle metaboreflex activation (MMA) would progressively attenuate spontaneous heart rate baroreflex sensitivity (SBRS). The animals were chronically instrumented to measure heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), mean and systolic arterial pressure (MAP and SAP), and left ventricular systolic pressures (LVSP) at rest and during mild or moderate treadmill exercise before and during progressive MMA [via graded reductions of hindlimb blood flow (HLBF)]. SBRS [slopes of the linear relationships (LRs) between HR and LVSP or SAP during spontaneous sequences of > or =3 consecutive beats when HR changed inversely vs. pressure] decreased during mild exercise from the resting values (-5.56 +/- 0.86 vs. -2.67 +/- 0.50 beats.min(-1).mmHg(-1), P <0.05), and in addition, these LRs were shifted upward. Progressive MMA gradually and linearly increased MAP, CO, and HR; linearly decreased SBRS; and shifted LRs upward and rightward to higher HR and pressures denoting baroreflex resetting. Moderate exercise caused a substantial reduction in SBRS (-1.57 +/- 0.38 beats.min(-1).mmHg(-1), P <0.05) and both an upward and rightward resetting. Gradual MMA at this higher workload also caused significant progressive increases in MAP, CO, and HR and progressive decreases in SBRS, and the LRs were shifted to higher MAP and HR. Our results demonstrate that gradual MMA during mild and moderate dynamic exercise progressively decreases SBRS. In addition, baroreflex control of HR is progressively reset to higher blood pressure and HR in proportion to the extent of MMA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Muscle metaboreflex attenuates spontaneous heart rate baroreflex sensitivity during dynamic exercise.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):H2867-73. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00043.2007. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17277032
-
Spontaneous baroreflex control of cardiac output during dynamic exercise, muscle metaboreflex activation, and heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Mar;294(3):H1310-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01187.2007. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18192212
-
Spontaneous baroreflex control of heart rate during exercise and muscle metaboreflex activation in heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Sep;293(3):H1929-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00564.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17604328
-
Altered reflex cardiovascular control during exercise in heart failure: animal studies.Exp Physiol. 2006 Jan;91(1):73-7. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2005.031179. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Exp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16179406 Review.
-
Mechanisms mediating muscle metaboreflex control of cardiac output during exercise: Impaired regulation in heart failure.Exp Physiol. 2025 May;110(5):675-685. doi: 10.1113/EP091752. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Exp Physiol. 2025. PMID: 38460125 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered calsequestrin glycan processing is common to diverse models of canine heart failure.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 May;377(1-2):11-21. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1560-7. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23456435
-
Effect of muscle metaboreflex activation on spontaneous cardiac baroreflex sensitivity during exercise in humans.J Physiol. 2011 Dec 15;589(Pt 24):6157-71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.219964. Epub 2011 Oct 3. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21969452 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Temporal relationships of blood pressure, heart rate, baroreflex function, and body temperature change over a hibernation bout in Syrian hamsters.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013 Oct 1;305(7):R759-68. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00450.2012. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23904107 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension depresses arterial baroreflex control of both heart rate and cardiac output during rest, exercise, and metaboreflex activation.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Nov 1;323(5):R720-R727. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00093.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36121147 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the role of group III/IV muscle afferents in the carotid baroreflex control of mean arterial pressure and heart rate during exercise.J Physiol. 2018 Apr 15;596(8):1373-1384. doi: 10.1113/JP275465. Epub 2018 Mar 2. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29388218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustyniak RA, Collins HL, Ansorge EJ, Rossi NF, O'Leary DS. Severe exercise alters the strength and mechanisms of the muscle metaboreflex. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280: H1645–H1652, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Barraco RA. Nucleus of the Solitary Tract. Boca Raton, FL: CRC, 1993
-
- Bertinieri G, Di Rienzo M, Cavallazzi A, Ferrari AU, Pedotti A, Mancia G. Evaluation of baroreceptor reflex by blood pressure monitoring in unanesthetized cats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 254: H377–H383, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Burger HR, Chandler MP, Rodenbaugh DW, Dicarlo SE. Dynamic exercise shifts the operating point and reduces the gain of the arterial baroreflex in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 275: R2043–R2048, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Coote JH, Dodds WN. The baroreceptor reflex and the cardiovascular changes associated with sustained muscular contraction in the cat. Pflügers Arch 363: 167–173, 1976 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

