Speckle myocardial imaging modalities for early detection of myocardial impairment in isolated left ventricular non-compaction
- PMID: 19966109
- PMCID: PMC3835601
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2009.182170
Speckle myocardial imaging modalities for early detection of myocardial impairment in isolated left ventricular non-compaction
Abstract
Objective: To examine the hypothesis that speckle myocardial imaging (SMI) modalities, including longitudinal, radial and circumferential systolic (s) and diastolic (d) myocardial velocity imaging, displacement (D), strain rate (SR) and strain (S), as well as left ventricular (LV) rotation/torsion are sensitive for detecting early myocardial dysfunction in isolated LV non-compaction (iLVNC).
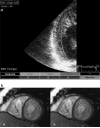
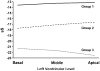
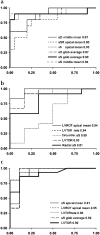
Design and results: Twenty patients with iLVNC diagnosed by cardiac magnetic resonance (15) or echocardiography (5) were included. Patients were divided into two groups: ejection fraction (EF)>50% (n=10) and EF<or=50% (n=10). Standard measures of systolic and diastolic function including pulsed wave tissue Doppler Imaging (PWTDI) were obtained. Longitudinal, radial and circumferential SMI, and LV rotation/torsion were compared with values for 20 age/sex-matched controls. EF, PWTDI E', E/E' and all of the SMI modalities were significantly abnormal for patients with EF<or=50% compared with controls. In contrast, EF and PWTDI E', E/E' were not significantly different between controls and patients with iLVNC (EF>50%). However, SMI-derived longitudinal sS, sSR, sD and radial sS, as well as LV rotation/torsion values, were all reduced in iLVNC (EF>50%) compared with controls. Measurements with the highest discriminating power between iLVNC (EF>50%) and controls were longitudinal sS mean of the six apical segments (area under the curve (AUC)=0.94), sS global average (AUC=0.94), LV rotation apical mean (AUC=0.94); LV torsion (AUC=0.93) LV torsion rate (AUC=0.94).
Conclusions: LV SMI values are reduced in patients with iLVNC, even those with normal EF and PWTDI. The most accurate SMI modalities to discriminate between patients and controls are longitudinal sS mean of the six apical segments, LV apical rotation or LV torsion rate.
Figures
References
-
- Chin TK, Perloff JK, Williams RG, et al. Isolated noncompaction of left ventricular myocardium. A study of eight cases. Circulation. 1990;82:507–13. - PubMed
-
- Petersen SE, Selvanayagam JB, Wiesmann F, et al. Left ventricular non-compaction: insights from cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:101–5. - PubMed
-
- Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, et al. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:1440–63. - PubMed
-
- Leitman M, Lysyansky P, Sidenko S, et al. Two-dimensional strain-a novel software for real-time quantitative echocardiographic assessment of myocardial function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2004;17:1021–9. - PubMed
-
- Park SJ, Miyazaki C, Bruce CJ, et al. Left ventricular torsion by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with diastolic dysfunction and normal ejection fraction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21:1129–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
