Antigenemia and specific IgM and IgG antibody responses in rabbits infected with Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 19967092
- PMCID: PMC2788723
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2009.47.4.409
Antigenemia and specific IgM and IgG antibody responses in rabbits infected with Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
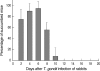
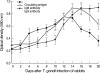
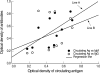
In this experiment, the correlation between antigenemia and specific antibody responses in Toxoplasma gondii-infected rabbits was assessed. We injected 1,000 T. gondii tachyzoites (RH) subcutaneously into 5 rabbits. Parasitemia, circulating antigens, and IgM and IgG antibody titers in blood were tested by ELISA and immunoblot. For detection of parasitemia, mice were injected with blood from rabbits infected with T. gondii and mice died between days 2 and 10 post-infection (PI). Circulating antigens were detected early on day 2 PI, and the titers increased from day 4 PI and peaked on day 12 PI. Anti-Toxoplasma IgM antibody titers increased on day 6 PI and peaked on days 14-16 PI. IgG was detected from day 10 PI, and the titers increased continuously during the experiment. The antigenic protein patterns differed during the infection period, and the number of bands increased with ongoing infection by the immunoblot analysis. These result indicated that Toxoplasma circulating antigens during acute toxoplasmosis are closely related to the presence of parasites in blood. Also, the circulating antigen levels were closely correlated with IgM titers, but not with IgG titers. Therefore, co-detection of circulating antigens with IgM antibodies may improve the reliability of the diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; antibody; antigenemia; parasitemia; rabbit.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of a Rec-ELISA using Toxoplasma gondii recombinant SporoSAG, BAG1, and GRA1 proteins in murine models infected orally with tissue cysts and oocysts.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 30;9(9):e108329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108329. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25268351 Free PMC article.
-
[Detection of Toxoplasma antigens and antibodies in mice infected with different strains of Toxoplasma gondii].Korean J Parasitol. 1995 Sep;33(3):201-10. doi: 10.3347/kjp.1995.33.3.201. Korean J Parasitol. 1995. PMID: 8528627 Korean.
-
Feline serum antibody responses to Toxoplasma gondii and characterization of target antigens.J Parasitol. 1994 Feb;80(1):73-80. J Parasitol. 1994. PMID: 8308661
-
Preparation of Toxoplasma gondii RH strain antigen, antigen analysis and antigen detection in sera: a review.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2001;32 Suppl 2:195-201. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2001. PMID: 12041589 Review.
-
Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms?Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 17;10(8):1659. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10081659. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36014077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological and Public Health Significance of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Wild Rabbits and Hares: 2010-2020.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 14;9(3):597. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030597. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33799419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from chickens from public markets in Pernambuco State, Brazil.Curr Res Parasitol Vector Borne Dis. 2024 Aug 14;6:100207. doi: 10.1016/j.crpvbd.2024.100207. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Parasitol Vector Borne Dis. 2024. PMID: 39253292 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of antigenic specificity of polyclonal antisera raised against Avibacterium paragallinarum by ELISA.Vet Anim Sci. 2020 May 16;9:100119. doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2020.100119. eCollection 2020 Jun. Vet Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32734120 Free PMC article.
-
The merits of designed ELISA avidity kit in detection of Toxoplasma gondii IgG antibody in laboratory conditions.Trop Parasitol. 2013 Jan;3(1):40-3. doi: 10.4103/2229-5070.113904. Trop Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23961440 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Toxoplasma gondii as a live vaccine vector in susceptible and resistant hosts.Parasit Vectors. 2011 Aug 28;4:168. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-4-168. Parasit Vectors. 2011. PMID: 21871123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajioka JW, Soldati D. Toxoplasma: Molecular and Cellular Biology. Norfolk, UK: Horizon Bioscience; 2007. pp. 37–58.
-
- Shaapan RM, El-Nawawi FA, Tawfik MA. Sensitivity and specificity of various serological tests for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in naturally infected sheep. Vet Parasitol. 2008;153:359–362. - PubMed
-
- Chen R, Lu S, Lou D, Lin A, Zeng X, Ding Z, Wen L, Ohta N, Wang J, Fu C. Evaluation of a rapid ELISA technique for detection of circulating antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbiol Immunol. 2008;52:180–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

