Anticoagulant activity of a sulfated galactan: serpin-independent effect and specific interaction with factor Xa
- PMID: 19967150
- PMCID: PMC2791905
- DOI: 10.1160/TH09-04-0273
Anticoagulant activity of a sulfated galactan: serpin-independent effect and specific interaction with factor Xa
Abstract
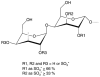
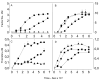
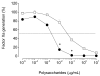
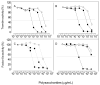
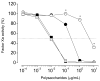
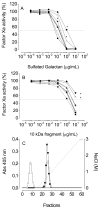
An algal sulfated galactan has high anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities. Its serpin-dependent anticoagulant action is due to promoting thrombin and factor (F)Xa inhibition by antithrombin and heparin cofactor II. Here, we evaluated the anticoagulant effect of the algal sulfated galactan using serpin-free plasma. In contrast to heparin, the sulfated galactan is still able to prolong coagulation time and delay thrombin and FXa generation in serpin-free plasma. We further investigated this effect using purified blood coagulation proteins, discovering that sulfated galactan inhibits the intrinsic tenase and prothrombinase complexes, which are critical for FXa and thrombin generation, respectively. We also investigated the mechanism by which sulfated galactan promotes FXa inhibition by antithrombin using specific recombinant mutants of the protease. We show that sulfated galactan interacts with the heparin-binding exosite of FXa and Arg-236 and Lys-240 of this site are critical residues for this interaction, as observed for heparin. Thus, sulfated galactan and heparin have similar high-affinity and specificity for interaction with FXa, though they have differences in their chemical structures. Similar to heparin, the ability of sulfated galactan to potentiate FXa inhibition by antithrombin is calcium-dependent. However, in contrast to heparin, this effect is not entirely dependent on the conformation of the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-rich domain of the protease. In conclusion, sulfated galactan and heparin have some similar effects on blood coagulation, but also differ significantly at the molecular level. This sulfated galactan opens new perspective for the development of antithrombotic drugs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Serpin-independent anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Sep;100(3):420-8. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18766257
-
Marine sulfated glycans with serpin-unrelated anticoagulant properties.Adv Clin Chem. 2013;62:269-303. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-800096-0.00007-x. Adv Clin Chem. 2013. PMID: 24772670
-
An algal sulfated galactan has an unusual dual effect on venous thrombosis due to activation of factor XII and inhibition of the coagulation proteases.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Mar;99(3):531-8. doi: 10.1160/TH07-10-0649. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18327401
-
Determinants of specificity of factor xa interaction with its physiological inhibitors.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006 Aug;6(8):859-65. doi: 10.2174/138955706777935017. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16918492 Review.
-
Targeting exosites on blood coagulation proteases.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2005 Jun;77(2):275-80. doi: 10.1590/s0001-37652005000200007. Epub 2005 May 9. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2005. PMID: 15895163 Review.
Cited by
-
Fractionation of sulfated galactan from the red alga Botryocladia occidentalis separates its anticoagulant and anti-SARS-CoV-2 properties.J Biol Chem. 2022 May;298(5):101856. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101856. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35337800 Free PMC article.
-
Fucanomics and galactanomics: marine distribution, medicinal impact, conceptions, and challenges.Mar Drugs. 2012 Apr;10(4):793-811. doi: 10.3390/md10040793. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Mar Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22690144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systems Pharmacology Model for Predicting Effects of Factor Xa Inhibitors in Healthy Subjects: Assessment of Pharmacokinetics and Binding Kinetics.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;4(11):650-9. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12035. Epub 2015 Oct 9. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26783501 Free PMC article.
-
Marine medicinal glycomics.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Jan 29;4:5. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00005. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24524028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific sulfation and glycosylation-a structural combination for the anticoagulation of marine carbohydrates.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Mar 6;4:33. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00033. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24639954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fareed J, Hoppensteadt DA. Heparins in the new millennium: Will unfractionated heparin survive? Semin Thromb Haemost. 2000;26:87–88. - PubMed
-
- Béguin S, Lindhout T, Hemker HC. The mode of action of heparin in plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1988;60:457–62. - PubMed
-
- Mourão PAS, Pereira MS. Searching for alternatives to heparin. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999;9:225–32. - PubMed
-
- Farias WRL, Valente AP, Pereira MS, Mourão PAS. Structure and anticoagulant activity of sulfated galactans - Isolation of a unique sulfated galactan from the red algae Botryocladia occidentalis and comparison of its anticoagulant action with that of sulfated galactans from invertebrates. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:29299–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

