Genetics of homocysteine metabolism and associated disorders
- PMID: 19967264
- PMCID: PMC3078648
- DOI: 10.1590/s0100-879x2009007500021
Genetics of homocysteine metabolism and associated disorders
Abstract
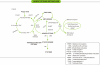
Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid derived from the metabolism of methionine, an essential amino acid, and is metabolized by one of two pathways: remethylation or transsulfuration. Abnormalities of these pathways lead to hyperhomocysteinemia. Hyperhomocysteinemia is observed in approximately 5% of the general population and is associated with an increased risk for many disorders, including vascular and neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune disorders, birth defects, diabetes, renal disease, osteoporosis, neuropsychiatric disorders, and cancer. We review here the correlation between homocysteine metabolism and the disorders described above with genetic variants on genes coding for enzymes of homocysteine metabolism relevant to clinical practice, especially common variants of the MTHFR gene, 677C>T and 1298A>C. We also discuss the management of hyperhomocysteinemia with folic acid supplementation and fortification of folic acid and the impact of a decrease in the prevalence of congenital anomalies and a decline in the incidence of stroke mortality.
References
-
- Selhub J. Homocysteine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 1999;19:217–246. - PubMed
-
- Mansoor MA, Bergmark C, Svardal AM, Lonning PE, Ueland PM. Redox status and protein binding of plasma homocysteine and other aminothiols in patients with early-onset peripheral vascular disease. Homocysteine and peripheral vascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15(2):232–240. - PubMed
-
- Frosst P, Blom HJ, Milos R, Goyette P, Sheppard CA, Mattews RG, et al. A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat Genet. 1995;10(1):111–113. - PubMed
-
- Jacques PF, Bostom AG, Williams RR, Ellison RC, Eckfeldt JH, Rosenberg IH, et al. Relation between folate status, a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, and plasma homocysteine concentrations. Circulation. 1996;93(1):7–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources