Vitrification of mouse embryos at 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell stages by cryotop method
- PMID: 19967554
- PMCID: PMC2799565
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-009-9370-2
Vitrification of mouse embryos at 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell stages by cryotop method
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of vitrification on the preimplantation developmental competence of mouse 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell stage embryos.
Methods: Mouse 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell stage embryos were cryopreserved using the cryotop vitrification method and subsequently warmed on a later date. The embryos were then assessed by their morphology, blastocyst formation and hatching rates. Additionally, trophectoderm (TE) and inner cell mass (ICM) cell numbers were compared in hatched blastocysts from the control and experimental groups.
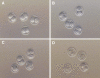
Results: Vitrified embryos at the 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell stages appeared morphologically normal after warming. The overall survival rate of vitrified embryos at various stages after warming was 96.7% and there were no significant differences among 2-cell stage (96.0%), 4-cell stage (96.8%) and 8-cell stage (97.1%) embryos (P > 0.05). The blastocyst formation rate (69.4%) and hatching rate (52.6%) of vitrified 2-cell embryos were significantly lower than that from the control group and vitrified 8-cell embryos (P < 0.05). In the vitrified 4-cell embryo group, the blastocyst formation rate (90.3%) was similar to the 8-cell group (91.2%), but the hatching rate (60.0%) was significantly lower than that of the non-vitrified control ( 84.1%) and vitrified 8-cell embryo (78.4%) groups (P < 0.05). When further development to the fully hatched blastocyst stage was compared, hatched blastocysts derived from vitrified 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell embryos had significantly lower cell counts both in the ICM and TE, as compared to fresh blastocysts (P < 0.05). Among the vitrified 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell embryo groups, there were no significant differences in the cell counts of ICM and TE (P > 0.05).
Conclusions: Although cryotop vitrification was suitable for the cryopreservation of mouse embryos from the 2-cell stage, 4-cell stage and 8-cell stage without significant loss of survival, vitrification had an adverse effect on the development of 2-cell embryos. Mouse embryos at the 8-cell stage had the best tolerance for vitrification and would yield the highest level of post-vitrification developmental competence among early cleavage stage embryos. Nevertheless, it is unclear how these findings can be extrapolated to human embryos.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of cryotop vitrification on preimplantation developmental competence of murine morula and blastocyst stage embryos.Reprod Biomed Online. 2009 Nov;19(5):708-13. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2009.09.006. Reprod Biomed Online. 2009. PMID: 20021719
-
Vitrification of mouse embryos at various stages by open-pulled straw (OPS) method.Anim Biotechnol. 2005;16(2):153-63. doi: 10.1080/10495390500263831. Anim Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16335809
-
Effect of the Re-Vitrification of Embryos at Different Stages on Embryonic Developmental Potential.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 14;12:653310. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.653310. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34335464 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of mice (Mus musculus L.) and hamster embryo development using culture and vitrification medium: Systematic review.Open Vet J. 2023 Feb;13(2):143-149. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i2.2. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Open Vet J. 2023. PMID: 37073251 Free PMC article.
-
The morphological and functional ultrastructure of cells in pre-implantation embryos.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2023 Jul;42(4):307-321. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2023011. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37449316 Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol enhances the clearance of mitochondrial damage by vitrification and improves the development of vitrified-warmed bovine embryos.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 18;13(10):e0204571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204571. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30335749 Free PMC article.
-
Digital microfluidic processing of mammalian embryos for vitrification.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 24;9(9):e108128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108128. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25250666 Free PMC article.
-
Which Stage of Mouse Embryos Is More Appropriate for Vitrification?Int J Fertil Steril. 2017 Jan-Mar;10(4):357-362. doi: 10.22074/ijfs.2016.5086. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Int J Fertil Steril. 2017. PMID: 28042416 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of The First Zygotic Cleavage Affects Post-Vitrification Viability of Murine Embryos Produced In Vivo.Int J Fertil Steril. 2015 Jul-Sep;9(2):221-9. doi: 10.22074/ijfs.2015.4243. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Int J Fertil Steril. 2015. PMID: 26246881 Free PMC article.
-
Oocytes Vitrification Using Automated Equipment Based on Microfluidic Chip.Ann Biomed Eng. 2025 Feb;53(2):471-480. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03623-9. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Ann Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 39320573
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/313573a0', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/313573a0'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3969158', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3969158/'}]}
- Rall WF, Fahy GM. Ice-free cryopreservation of mouse embryos at −196°C by vitrification. Nature. 1985;313:573–5. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16792858', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16792858/'}]}
- Vajta G, Nagy ZP. Are programmable freezers still needed in the embryo laboratory? Review on vitrification. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;12:779–96. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2307246', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2307246/'}]}
- Gordts S, Roziers P, Campo R, Noto V. Survival and pregnancy outcome after ultrarapid freezing of human embryos. Fertil Steril. 1990;53:469–72. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.theriogenology.2006.09.014', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2006.09.014'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17055564', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17055564/'}]}
- Kuwayama M. Highly efficient vitrification for cryopreservationof human oocytes and embryos: the Cryotop method. Theriogenology. 2007;67:73–80. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16176668', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16176668/'}]}
- Kuwayama M, Vajta G, Kato O, Leibo SP. Highly efficient vitrification method for cryopreservation of human oocytes. Reprod Biomed Online. 2005;11:300–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

