A gene expression signature that predicts the therapeutic response of the basal-like breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- PMID: 19967557
- PMCID: PMC3965252
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-009-0664-y
A gene expression signature that predicts the therapeutic response of the basal-like breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Abstract
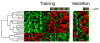
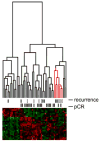
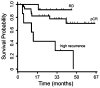
Several gene expression profiles have been reported to predict breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. These studies often consider breast cancer as a homogeneous entity, although higher rates of pathologic complete response (pCR) are known to occur within the basal-like subclass. We postulated that profiles with higher predictive accuracy could be derived from a subset analysis of basal-like tumors in isolation. Using a previously described "intrinsic" signature to differentiate breast tumor subclasses, we identified 50 basal-like tumors from two independent clinical trials associated with gene expression profile data. 24 tumor data sets were derived from a 119-patient neoadjuvant trial at our institution and an additional 26 tumor data sets were identified from a published data set (Hess et al. J Clin Oncol 24:4236-4244, 2006). The combined 50 basal-like tumors were partitioned to form a 37 sample training set with 13 sequestered for validation. Clinical surveillance occurred for a mean of 26 months. We identified a 23-gene profile which predicted pCR in basal-like breast cancers with 92% predictive accuracy in the sequestered validation data set. Furthermore, distinct cluster of patients with high rates of cancer recurrence was observed based on cluster analysis with the 23-gene signature. Disease-free survival analysis of these three clusters revealed significantly reduced survival in the patients of this high recurrence cluster. We identified a 23-gene signature which predicts response of basal-like breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy as well as disease-free survival. This signature is independent of tissue collection method and chemotherapeutic regimen.
Figures


References
-
- Bertucci F, Finetti P, Rougemont J, Charafe-Jauffret E, Nasser V, Loriod B, Camerlo J, Tagett R, Tarpin C, Houvenaeghel G, et al. Gene expression profiling for molecular characterization of inflammatory breast cancer and prediction of response to chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2004;64(23):8558–8565. - PubMed
-
- Hannemann J, Oosterkamp HM, Bosch CAJ, Velds A, Wessels LFA, Loo C, Rutgers EJ, Rodenhuis S, van de Vijver MJ. Changes in gene expression associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(15):3331–3342. - PubMed
-
- Thuerigen O, Schneeweiss A, Toedt G, Warnat P, Hahn M, Kramer H, Brors B, Rudlowski C, Benner A, Schuetz F, et al. Gene expression signature predicting pathologic complete response with gemcitabine, epirubicin, and docetaxel in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(12):1839–1845. - PubMed
-
- Hess KR, Anderson K, Symmans WF, Valero V, Ibrahim N, Mejia JA, Booser D, Theriault RL, Buzdar AU, Dempsey PJ, et al. Pharmacogenomic predictor of sensitivity to preoperative chemotherapy with paclitaxel and fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(26):4236–4244. - PubMed
-
- Ayers M, Symmans WF, Stec J, Damokosh AI, Clark E, Hess K, Lecocke M, Metivier J, Booser D, Ibrahim N, et al. Gene expression profiles predict complete pathologic response to neoadjuvant paclitaxel and fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(12):2284–2293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

