Involvement of cyclin B1 in progesterone-mediated cell growth inhibition, G2/M cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in human endometrial cell
- PMID: 19968870
- PMCID: PMC2797512
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-7-144
Involvement of cyclin B1 in progesterone-mediated cell growth inhibition, G2/M cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in human endometrial cell
Abstract
Background: Progesterone plays an important role in the proliferation and differentiation of human endometrial cells (hECs). Large-dose treatment with progesterone has been used for treatment of endometrial proliferative disorders. However, the mechanisms behind remain unknown.
Methods: To investigate the role of cyclin B1 in proliferation and differentiation of hECs in menstrual cycle, the expression of cyclin B1 throughout the menstrual cycle was evaluated in hECs. To determine the effects of progesterone on the proliferation, cell cycle progression and apoptosis of hECs and to test if cyclin B1 is involved in these effects, progesterone and/or Alsterpaullone (Alp, a specific inhibitor of Cyclin B1/Cdc2) were added to primary hECs. Cellular proliferation was evaluated with MTT test, cell cycle with propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cytometry, apoptosis with FITC-Annexin V and the expression of cyclin B1 with Western blotting.
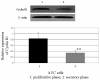
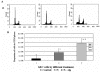
Results: The expression level of cyclin B1 in secretory endometria was significantly lower than in proliferative endometria (p < 0.01). Progesterone significantly inhibited the growth of hECs in a concentration-dependent manner (P < 0.01). The treatment with progesterone significantly decreased the expression of cyclin B1, increased the proportions of cell in G2/M phase, and apoptotic cells (P < 0.05 for all). The presence of Alp significantly enhanced the effects of progesterone on cyclin B1 down-regulation, G2/M cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis (P < 0.01 for all).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that cyclin B1 is a critical factor in proliferation and differentiation of hECs. Progesterone may inhibit cell proliferation, mediate G2/M cell cycle arrest and induce apoptosis in hECs via down-regulating Cyclin B1.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of triethylene glycol dimethacrylate on the cytotoxicity, cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostanoids production in human dental pulp cells.Int Endod J. 2012 Sep;45(9):848-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2012.02042.x. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Int Endod J. 2012. PMID: 22486746
-
15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J2 inhibits G2-M phase progression in human breast cancer cells via the down-regulation of cyclin B1 and survivin expression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 May;102(3):263-73. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9336-3. Epub 2006 Sep 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. PMID: 17028981
-
Oroxylin A induces G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest via inhibiting Cdk7-mediated expression of Cdc2/p34 in human gastric carcinoma BGC-823 cells.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2008 Nov;60(11):1459-63. doi: 10.1211/jpp/60.11.0006. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18957166
-
Anti-proliferative effect of polysaccharides from Salicornia herbacea on induction of G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009 Nov;19(11):1482-9. doi: 10.4014/jmb.0902.063. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19996705
-
Estrogen and progesterone lower cyclin B1 AND D1 expression, block cell cycle in G2/M, and trigger apoptosis in human adrenal carcinoma cell cultures.Horm Metab Res. 2008 May;40(5):306-10. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1073140. Horm Metab Res. 2008. PMID: 18491248
Cited by
-
Overexpression of cyclin B1 antagonizes chemotherapeutic-induced apoptosis through PTEN/Akt pathway in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Jan;14(1):45-55. doi: 10.4161/cbt.22627. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23114644 Free PMC article.
-
PARP inhibitor re‑sensitizes Adriamycin resistant leukemia cells through DNA damage and apoptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jan;19(1):75-84. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9628. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30431088 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of N-arylsulfonyl carbazoles as novel anticancer agents.RSC Adv. 2018 May 10;8(31):17183-17190. doi: 10.1039/c8ra02939c. eCollection 2018 May 9. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35539273 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Thienyl-Based Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Pers Med. 2022 May 1;12(5):738. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050738. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629160 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Function of WNT6: From Development to Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 9;8:558155. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.558155. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33425886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lindahl B, Willen R. Endometrial hyperplasia. Clinico-pathological considerations of a prospective randomised study after abrasio only or high-dose gestagen treatment. Results of 2 years follow-up of 292 patients. Anticancer Res. 1991;11:403–406. - PubMed
-
- Thigpen JT, Brady MF, Alvarez RD, Adelson MD, Homesley HD, Manetta A, Soper JT, Given FT. Oral medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma: a dose-response study by the Gynecologic Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1736–1744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

