Modified H5 promoter improves stability of insert genes while maintaining immunogenicity during extended passage of genetically engineered MVA vaccines
- PMID: 19969118
- PMCID: PMC2821965
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.11.056
Modified H5 promoter improves stability of insert genes while maintaining immunogenicity during extended passage of genetically engineered MVA vaccines
Abstract
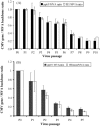
We have engineered recombinant (r) Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) to express multiple antigens under the control of either of two related vaccinia synthetic promoters (pSyn) with early and late transcriptional activity or the modified H5 (mH5) promoter which has predominant early activity. We sequentially passaged these constructs and analyzed their genetic stability by qPCR, and concluded that rMVA expressing multiple antigens using the mH5 promoter exhibit remarkable genetic stability and maintain potent immunogenicity after serial passage. In contrast, rMVA expressing antigens using engineered vaccinia synthetic E/L (pSyn I or II) promoters are genetically unstable. Progressive accumulation of antigen loss variants resulted in a viral preparation with lower immunogenicity after serial passage. Metabolic labeling, followed by cold chase revealed little difference in stability of proteins expressed from mH5 or pSyn promoter constructs. We conclude that maintenance of genetic stability which is achieved using mH5, though not with pSyn promoters, is linked to timing, not the magnitude of expression levels of foreign antigen, which is more closely associated with immunogenicity of the vaccine.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhancing cellular immunogenicity of MVA-vectored vaccines by utilizing the F11L endogenous promoter.Vaccine. 2016 Jan 2;34(1):49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.11.028. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 26616553
-
Poxviral promoters for improving the immunogenicity of MVA delivered vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(1):203-209. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1513439. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30148692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-expressing GP5 and M proteins under different promoters in recombinant modified vaccinia virus ankara (rMVA)-based vaccine vector enhanced the humoral and cellular immune responses of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV).Virus Genes. 2007 Dec;35(3):585-95. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0161-5. Epub 2007 Oct 6. Virus Genes. 2007. PMID: 17922181 Free PMC article.
-
Transgene expression knock-down in recombinant Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara vectors improves genetic stability and sustained transgene maintenance across multiple passages.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 6;15:1338492. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1338492. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38380318 Free PMC article.
-
Pox viruses as eukaryotic cloning and expression vectors: future medical and veterinary vaccines.Prog Vet Microbiol Immunol. 1988;4:197-217. Prog Vet Microbiol Immunol. 1988. PMID: 3078866 Review.
Cited by
-
Newly Designed Poxviral Promoters to Improve Immunogenicity and Efficacy of MVA-NP Candidate Vaccines against Lethal Influenza Virus Infection in Mice.Pathogens. 2023 Jun 23;12(7):867. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12070867. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37513714 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus complement control protein (KCP) and glycoprotein K8.1 are not required for viral infection in vitro or in vivo.J Virol. 2024 Jun 13;98(6):e0057624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00576-24. Epub 2024 May 20. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38767375 Free PMC article.
-
Protection of IFNAR (-/-) mice against bluetongue virus serotype 8, by heterologous (DNA/rMVA) and homologous (rMVA/rMVA) vaccination, expressing outer-capsid protein VP2.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e60574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060574. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593251 Free PMC article.
-
A novel vaccine against Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever protects 100% of animals against lethal challenge in a mouse model.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 12;9(3):e91516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091516. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24621656 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of recombinant MVA-norovirus: a comparison study of bacterial artificial chromosome- and marker-based systems.Virol J. 2019 Aug 9;16(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1212-y. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31399106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sutter G., Staib C. Vaccinia vectors as candidate vaccines: the development of modified vaccinia virus Ankara for antigen delivery. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2003;3(3):263–271. - PubMed
-
- Stickl H., Hochstein-Mintzel V., Mayr A., Huber H.C., Schafer H., Holzner A. MVA vaccination against smallpox: clinical tests with an attenuated live vaccinia virus strain (MVA) (author's transl.) Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1974;99(47):2386–2392. - PubMed
-
- Werner G.T., Jentzsch U., Metzger E., Simon J. Studies on poxvirus infections in irradiated animals. Arch Virol. 1980;64(3):247–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

