Mutations in the CDP-choline pathway for phospholipid biosynthesis bypass the requirement for an essential phospholipid transfer protein
- PMID: 1997207
- PMCID: PMC7802412
- DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90508-v
Mutations in the CDP-choline pathway for phospholipid biosynthesis bypass the requirement for an essential phospholipid transfer protein
Abstract
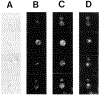
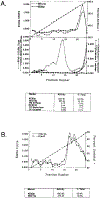
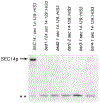
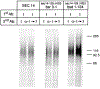
SEC14p is the yeast phosphatidylinositol (PI)/phosphatidylcholine (PC) transfer protein, and it effects an essential stimulation of yeast Golgi secretory function. We now report that the SEC14p localizes to the yeast Golgi and that the SEC14p requirement can be specifically and efficiently bypassed by mutations in any one of at least six genes. One of these suppressor genes was the structural gene for yeast choline kinase (CKI), disruption of which rendered the cell independent of the normally essential SEC14p requirement. The antagonistic action of the CKI gene product on SEC14p function revealed a previously unsuspected influence of biosynthetic activities of the CDP-choline pathway for PC biosynthesis on yeast Golgi function and indicated that SEC14p controls the phospholipid content of yeast Golgi membranes in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Aitken JF, van Heusden GPH, Temkin M, and Dowhan W (1990). The gene encoding the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein is essential for cell growth. J. Biol. Chem 265, 4711–4717. - PubMed
-
- Bankaitis VA, Aitken JF, Cleves AE, and Dowhan W (1990). An essential role for a phospholipid transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature 347, 561–562. - PubMed
-
- Botstein D, Falco SC, Stewart S, Brennan M, Scherer S, Stinch-comb DI, Struhl K, and Davis R (1979). Sterile host yeast (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene 8, 17–24. - PubMed
-
- Bowman B, and Slayman CW (1979). The effects of vanadate on the plasma membrane ATPase of Neurospora crassa. J. Biol. Chem 254, 2928–2934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

