Kilovoltage beam Monte Carlo dose calculations in submillimeter voxels for small animal radiotherapy
- PMID: 19994508
- PMCID: PMC2773455
- DOI: 10.1118/1.3238465
Kilovoltage beam Monte Carlo dose calculations in submillimeter voxels for small animal radiotherapy
Abstract
Purpose: Small animal conformal radiotherapy (RT) is essential for preclinical cancer research studies and therefore various microRT systems have been recently designed. The aim of this paper is to efficiently calculate the dose delivered using our microRT system based on a microCT scanner with the Monte Carlo (MC) method and to compare the MC calculations to film measurements.
Methods: Doses from 2-30 mm diameter 120 kVp photon beams deposited in a solid water phantom with 0.2 x 0.2 x 0.2 mm3 voxels are calculated using the latest versions of the EGSnrc codes BEAMNRC and DOSXYZNRC. Two dose calculation approaches are studied: a two-step approach using phase-space files and direct dose calculation with BEAMNRC simulation sources. Due to the small beam size and submillimeter voxel size resulting in long calculation times, variance reduction techniques are studied. The optimum bremsstrahlung splitting number (NBRSPL in BEAMNRC) and the optimum DOSXYZNRC photon splitting (Nsplit) number are examined for both calculation approaches and various beam sizes. The dose calculation efficiencies and the required number of histories to achieve 1% statistical uncertainty--with no particle recycling--are evaluated for 2-30 mm beams. As a final step, film dose measurements are compared to MC calculated dose distributions.
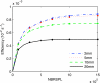
Results: The optimum NBRSPL is approximately 1 x 10(6) for both dose calculation approaches. For the dose calculations with phase-space files, Nsplit varies only slightly for 2-30 mm beams and is established to be 300. Nsplit for the DOSXYZNRC calculation with the BEAMNRC source ranges from 300 for the 30 mm beam to 4000 for the 2 mm beam. The calculation time significantly increases for small beam sizes when the BEAMNRC simulation source is used compared to the simulations with phase-space files. For the 2 and 30 mm beams, the dose calculations with phase-space files are more efficient than the dose calculations with BEAMNRC sources by factors of 54 and 1.6, respectively. The dose calculation efficiencies converge for beams with diameters larger than 30 mm.
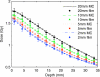
Conclusions: A very good agreement of MC calculated dose distributions to film measurements is found. The mean difference of percentage depth dose curves between calculated and measured data for 2, 5, 10, and 20 mm beams is 1.8%.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficient photon beam dose calculations using DOSXYZnrc with BEAMnrc.Med Phys. 2006 Aug;33(8):3046-56. doi: 10.1118/1.2219778. Med Phys. 2006. PMID: 16964882
-
Fast, accurate photon beam accelerator modeling using BEAMnrc: a systematic investigation of efficiency enhancing methods and cross-section data.Med Phys. 2009 Dec;36(12):5451-66. doi: 10.1118/1.3253300. Med Phys. 2009. PMID: 20095258 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of latent variances in Monte Carlo dose calculations with Varian TrueBeam photon phase-spaces used as a particle source.Phys Med Biol. 2017 Dec 29;63(1):01NT03. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa9f39. Phys Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29205177
-
Monte Carlo simulations in radiotherapy dosimetry.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Jun 27;13(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1065-3. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29945636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reflections on a life with Monte Carlo in Medical Physics.Med Phys. 2023 Jun;50 Suppl 1:91-94. doi: 10.1002/mp.16278. Epub 2023 Feb 18. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36779658 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the effects of treatment planning variables in small animal radiotherapy dose distributions.Med Phys. 2010 Feb;37(2):590-9. doi: 10.1118/1.3276738. Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 20229867 Free PMC article.
-
Modality comparison for small animal radiotherapy: a simulation study.Med Phys. 2014 Jan;41(1):011710. doi: 10.1118/1.4842415. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24387502 Free PMC article.
-
A novel technique for image-guided local heart irradiation in the rat.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Dec;13(6):593-603. doi: 10.7785/tcrtexpress.2013.600256. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2014. PMID: 24000983 Free PMC article.
-
Monte Carlo simulations of EBT3 film dose deposition for percentage depth dose (PDD) curve evaluation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020 Dec;21(12):314-324. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13078. Epub 2020 Nov 6. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 33155768 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of tissue segmentation for dose calculations for kilovoltage radiation therapy.Med Phys. 2011 Jun;38(6):3039-49. doi: 10.1118/1.3589138. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21815377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan M., Hill R., and Vandyk J., “Partial volume rat lung irradiation: An evaluation of early DNA damage,” Int. J. Radiat. Oncol., Biol., Phys. IOBPD3 40, 467–476 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Hillman G. G., Maughan R. L., Grignon D. J., Yudelev M., Rubio J., Tekyi-Mensah S., Layer A., Che M., and Forman J. D., “Neutron or photon irradiation for prostate tumors: enhancement of cytokine therapy in a metastatic tumor model,” Clin. Cancer Res. ZZZZZZ 7, 136–144 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

