The amnesiac gene is involved in the regulation of thermal nociception in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 19995327
- PMCID: PMC3032918
- DOI: 10.3109/01677060903419751
The amnesiac gene is involved in the regulation of thermal nociception in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
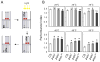
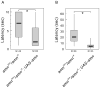
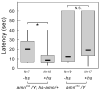
Nociception is a mechanism fundamental to the ability of animals to avoid noxious stimuli capable of causing serious tissue damage. It has been established that in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, the transient receptor potential (TRP) channel encoded by the painless gene (pain) is required for detecting thermal and mechanical noxious stimuli. Little is known, however, about other genetic components that control nociceptive behaviors in Drosophila. The amnesiac gene (amn), which encodes a putative neuropeptide precursor, is important for stabilizing olfactory memory, and is involved in various aspects of other associative and nonassociative learning. Previous studies have indicated that amn also regulates ethanol sensitivity and sleep. Here the authors show that amn plays an additional critical role in nociception. Their data show that amn mutant larvae and adults are significantly less responsive to noxious heat stimuli (greater than approximately 40 degrees C) than their wild-type counterparts. The phenotype of amn mutants in thermal nociception, which closely resembles that of pain mutants, was phenocopied in flies expressing amn RNAi, and this phenotype was rescued by the expression of a wild-type amn transgene. These results provide compelling evidence that amn is a novel genetic component of the mechanism that regulates thermal nociception in Drosophila.
Figures

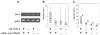
References
-
- Caldwell PE, Walkiewicz M, Stern M. Ras activity in the Drosophila prothoracic gland regulates body size and developmental rate via ecdysone release. Curr Biol. 2005;15:1785–1795. - PubMed
-
- Feany MB, Quinn WG. A neuropeptide gene defined by the Drosophila memory mutant amnesiac. Science. 1995;268:869–873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
