Multiple innate signaling pathways cooperate with CD40 to induce potent, CD70-dependent cellular immunity
- PMID: 19995538
- PMCID: PMC2822033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.11.071
Multiple innate signaling pathways cooperate with CD40 to induce potent, CD70-dependent cellular immunity
Abstract
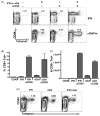
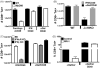
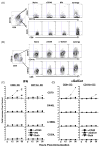
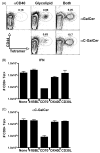
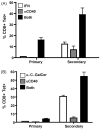
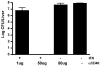
We have previously shown that Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists cooperate with CD40 to generate CD8 T cell responses exponentially larger than the responses generated with traditional vaccine formulations. We have also shown that combined TLR agonist/anti-CD40 immunization uniquely induces the upregulation of CD70 on antigen bearing dendritic cells (DCs). In contrast, immunization with either a TLR agonist or a CD40 stimulus alone does not significantly increase CD70 expression on DCs. Furthermore, the CD8(+) T cell response generated by combined TLR agonist/anti-CD40 immunization is dependent on the expression of CD70 by DCs, as CD70 blockade following immunization dramatically decreases the CD8 T cell response. Here we show that other innate pathways, independent of the TLRs, can also cooperate with CD40 to induce potent, CD70 dependent, CD8 T cell responses. These innate stimuli include Type I IFN (IFN) and alpha-galactosylceramide (alphaGalCer) or aC-GalCer, glycolipids that are presented by a nonclassical class I MHC molecule, CD1d, and are able to activate NKT cells. Furthermore, this combined IFN/anti-CD40 immunization generates protective memory against bacterial challenge with Listeria monocytogenes. Together these data indicate the importance of assessing CD70 expression on DCs as a marker for the capacity of a given vaccine formulation to potently activate cellular immunity. Our data indicate that optimal induction of CD70 expression requires a coordinated stimulation of both innate (TLR, IFN, alphaGalCer) and adaptive (CD40) signaling pathways.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Edwards AD, Diebold SS, Slack EM, Tomizawa H, Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Akira S, Reis e Sousa C. Toll-like receptor expression in murine DC subsets: lack of TLR7 expression by CD8 alpha+ DC correlates with unresponsiveness to imidazoquinolines. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:827–833. - PubMed
-
- Edwards AD, Manickasingham SP, Sporri R, Diebold SS, Schulz O, Sher A, Kaisho T, Akira S, Reis e Sousa C. Microbial recognition via Toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent pathways determines the cytokine response of murine dendritic cell subsets to CD40 triggering. J Immunol. 2002;169:3652–3660. - PubMed
-
- Zhu J, Huang X, Yang Y. Type I IFN signaling on both B and CD4 T cells is required for protective antibody response to adenovirus. J Immunol. 2007;178:3505–3510. - PubMed
-
- Hervas-Stubbs S, Rueda P, Lopez L, Leclerc C. Insect baculoviruses strongly potentiate adaptive immune responses by inducing type I IFN. J Immunol. 2007;178:2361–2369. - PubMed
-
- Fink K, Lang KS, Manjarrez-Orduno N, Junt T, Senn BM, Holdener M, Akira S, Zinkernagel RM, Hengartner H. Early type I interferon-mediated signals on B cells specifically enhance antiviral humoral responses. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:2094–2105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

