Evaluation of flagella and flagellin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as vaccines
- PMID: 19995892
- PMCID: PMC2812208
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00806-09
Evaluation of flagella and flagellin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as vaccines
Abstract
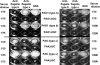
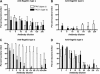
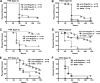
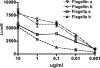
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a serious pathogen in hospitalized, immunocompromised, and cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. P. aeruginosa is motile via a single polar flagellum made of polymerized flagellin proteins differentiated into two major serotypes: a and b. Antibodies to flagella delay onset of infection in CF patients, but whether immunity to polymeric flagella and that to monomeric flagellin are comparable has not been addressed, nor has the question of whether such antibodies might negatively impact Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) activation, an important component of innate immunity to P. aeruginosa. We compared immunization with flagella and that with flagellin for in vitro effects on motility, opsonic killing, and protective efficacy using a mouse pneumonia model. Antibodies to flagella were superior to antibodies to flagellin at inhibiting motility, promoting opsonic killing, and mediating protection against P. aeruginosa pneumonia in mice. Protection against the flagellar type strains PAK and PA01 was maximal, but it was only marginal against motile clinical isolates from flagellum-immunized CF patients who nonetheless became colonized with P. aeruginosa. Purified flagellin was a more potent activator of TLR5 than were flagella and also elicited higher TLR5-neutralizing antibodies than did immunization with flagella. Antibody to type a but not type b flagella or flagellin inhibited TLR5 activation by whole bacterial cells. Overall, intact flagella appear to be superior for generating immunity to P. aeruginosa, and flagellin monomers might induce antibodies capable of neutralizing innate immunity due to TLR5 activation, but solid immunity to P. aeruginosa based on flagellar antigens may require additional components beyond type a and type b proteins from prototype strains.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson, T. R., and T. C. Montie. 1989. Flagellar antibody stimulated opsonophagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with response to either a-type or b-type flagellar antigen. Can. J. Microbiol. 35:890-894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

