Overall Cdk activity modulates the DNA damage response in mammalian cells
- PMID: 19995934
- PMCID: PMC2806328
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200903033
Overall Cdk activity modulates the DNA damage response in mammalian cells
Abstract
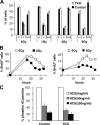
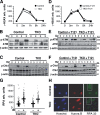
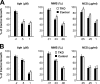
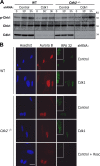
In response to DNA damage, cells activate a phosphorylation-based signaling cascade known as the DNA damage response (DDR). One of the main outcomes of DDR activation is inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) activity to restrain cell cycle progression until lesions are healed. Recent studies have revealed a reverse connection by which Cdk activity modulates processing of DNA break ends and DDR activation. However, the specific contribution of individual Cdks to this process remains poorly understood. To address this issue, we have examined the DDR in murine cells carrying a defined set of Cdks. Our results reveal that genome maintenance programs of postreplicative cells, including DDR, are regulated by the overall level of Cdk activity and not by specific Cdks.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

