Mitosomes in Entamoeba histolytica contain a sulfate activation pathway
- PMID: 19995967
- PMCID: PMC2799805
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907106106
Mitosomes in Entamoeba histolytica contain a sulfate activation pathway
Abstract
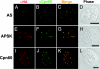
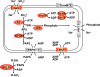
Hydrogenosomes and mitosomes are mitochondrion-related organelles in anaerobic/microaerophilic eukaryotes with highly reduced and divergent functions. The full diversity of their content and function, however, has not been fully determined. To understand the central role of mitosomes in Entamoeba histolytica, a parasitic protozoon that causes amoebic dysentery and liver abscesses, we examined the proteomic profile of purified mitosomes. Using 2 discontinuous Percoll gradient centrifugation and MS analysis, we identified 95 putative mitosomal proteins. Immunofluorescence assay showed that 3 proteins involved in sulfate activation, ATP sulfurylase, APS kinase, and inorganic pyrophosphatase, as well as sodium/sulfate symporter, involved in sulfate uptake, were compartmentalized to mitosomes. We have also provided biochemical evidence that activated sulfate derivatives, adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate and 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate, were produced in mitosomes. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the aforementioned proteins and chaperones have distinct origins, suggesting the mosaic character of mitosomes in E. histolytica consisting of proteins derived from alpha-proteobacterial, delta-proteobacterial, and ancestral eukaryotic origins. These results suggest that sulfate activation is the major function of mitosomes in E. histolytica and that E. histolytica mitosomes represent a unique mitochondrion-related organelle with remarkable diversity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- van der Giezen M. Hydrogenosomes and mitosomes: conservation and evolution of functions. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2009;56:221–231. - PubMed
-
- Aguilera P, Barry T, Tovar J. Entamoeba histolytica mitosomes: organelles in search of a function. Exp Parasitol. 2008;118:10–16. - PubMed
-
- Lindmark DG, Muller M. Hydrogenosome, a cytoplasmic organelle of the anaerobic flagellate Tritrichomonas foetus, and its role in pyruvate metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1973;248:7724–7728. - PubMed
-
- Hrdy I, et al. Trichomonas hydrogenosomes contain the NADH dehydrogenase module of mitochondrial complex I. Nature. 2004;432:618–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

