ChIP-Seq of transcription factors predicts absolute and differential gene expression in embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 19995984
- PMCID: PMC2789751
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0904863106
ChIP-Seq of transcription factors predicts absolute and differential gene expression in embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Next-generation sequencing has greatly increased the scope and the resolution of transcriptional regulation study. RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) and ChIP-Seq experiments are now generating comprehensive data on transcript abundance and on regulator-DNA interactions. We propose an approach for an integrated analysis of these data based on feature extraction of ChIP-Seq signals, principal component analysis, and regression-based component selection. Compared with traditional methods, our approach not only offers higher power in predicting gene expression from ChIP-Seq data but also provides a way to capture cooperation among regulators. In mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs), we find that a remarkably high proportion of variation in gene expression (65%) can be explained by the binding signals of 12 transcription factors (TFs). Two groups of TFs are identified. Whereas the first group (E2f1, Myc, Mycn, and Zfx) act as activators in general, the second group (Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, Smad1, Stat3, Tcfcp2l1, and Esrrb) may serve as either activator or repressor depending on the target. The two groups of TFs cooperate tightly to activate genes that are differentially up-regulated in ESCs. In the absence of binding by the first group, the binding of the second group is associated with genes that are repressed in ESCs and derepressed upon early differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

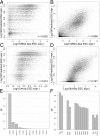
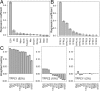
References
-
- Mortazavi A, et al. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5:621–628. - PubMed
-
- Cloonan N, et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat Methods. 2008;5:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DS, Mortazavi A, Myers RM, Wold B. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science. 2007;316:1497–1502. - PubMed
-
- Bussemaker HJ, Li H, Siggia ED. Regulatory element detection using correlation with expression. Nat Genet. 2001;27:167–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

