Phospholipase C-related but catalytically inactive protein is required for insulin-induced cell surface expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors
- PMID: 19996098
- PMCID: PMC2836089
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.070045
Phospholipase C-related but catalytically inactive protein is required for insulin-induced cell surface expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors
Abstract
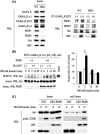
The gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) receptors play a pivotal role in fast synaptic inhibition in the central nervous system. One of the key factors for determining synaptic strength is the number of receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, which is maintained by the balance between cell surface insertion and endocytosis of the receptors. In this study, we investigated whether phospholipase C-related but catalytically inactive protein (PRIP) is involved in insulin-induced GABA(A) receptor insertion. Insulin potentiated the GABA-induced Cl(-) current (I(GABA)) by about 30% in wild-type neurons, but not in PRIP1 and PRIP2 double-knock-out (DKO) neurons, suggesting that PRIP is involved in insulin-induced potentiation. The phosphorylation level of the GABA(A) receptor beta-subunit was increased by about 30% in the wild-type neurons but not in the mutant neurons, which were similar to the changes observed in I(GABA). We also revealed that PRIP recruited active Akt to the GABA(A) receptors by forming a ternary complex under insulin stimulation. The disruption of the binding between PRIP and the GABA(A) receptor beta-subunit by PRIP interference peptide attenuated the insulin potentiation of I(GABA). Taken together, these results suggest that PRIP is involved in insulin-induced GABA(A) receptor insertion by recruiting active Akt to the receptor complex.
Figures




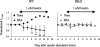

Similar articles
-
Modulation of GABA(A) receptor phosphorylation and membrane trafficking by phospholipase C-related inactive protein/protein phosphatase 1 and 2A signaling complex underlying brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent regulation of GABAergic inhibition.J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 4;281(31):22180-22189. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603118200. Epub 2006 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16754670
-
Phospholipase C-related inactive protein is involved in trafficking of gamma2 subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors to the cell surface.J Neurosci. 2007 Feb 14;27(7):1692-701. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3155-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17301177 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C-related inactive protein is implicated in the constitutive internalization of GABAA receptors mediated by clathrin and AP2 adaptor complex.J Neurochem. 2007 May;101(4):898-905. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04399.x. Epub 2007 Jan 24. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17254016
-
Regulation of GABA(A)-receptor surface expression with special reference to the involvement of GABARAP (GABA(A) receptor-associated protein) and PRIP (phospholipase C-related, but catalytically inactive protein).J Pharmacol Sci. 2007 Aug;104(4):285-92. doi: 10.1254/jphs.cp0070063. Epub 2007 Aug 10. J Pharmacol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17690529 Review.
-
GABAA receptor associated proteins: a key factor regulating GABAA receptor function.J Neurochem. 2007 Jan;100(2):279-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04206.x. Epub 2006 Nov 2. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17083446 Review.
Cited by
-
DOT1L protects against podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease through phospholipase C-like 1.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 25;22(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01895-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39456056 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of GABAARs by phosphorylation.Adv Pharmacol. 2015;72:97-146. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Adv Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25600368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase C-related but catalytically inactive protein (PRIP) modulates synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (SNAP-25) phosphorylation and exocytosis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):10565-10578. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.294645. Epub 2012 Feb 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22311984 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C-related catalytically inactive protein (PRIP) controls KIF5B-mediated insulin secretion.Biol Open. 2014 May 8;3(6):463-74. doi: 10.1242/bio.20147591. Biol Open. 2014. PMID: 24812354 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C-related Catalytically Inactive Protein Is a New Modulator of Thermogenesis Promoted by β-Adrenergic Receptors in Brown Adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 19;291(8):4185-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.705723. Epub 2015 Dec 25. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26706316 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

