Identification of a suppressive mechanism for Hedgehog signaling through a novel interaction of Gli with 14-3-3
- PMID: 19996099
- PMCID: PMC2823557
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038232
Identification of a suppressive mechanism for Hedgehog signaling through a novel interaction of Gli with 14-3-3
Abstract
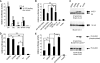
Gli transcription factors are central effectors of Hedgehog signaling in development and tumorigenesis. Using a tandem affinity purification (TAP) strategy and mass spectrometry, we have found that Gli1 interacts with 14-3-3epsilon, and that Gli2 and Gli3 also bind to 14-3-3epsilon through homologous sites. This interaction depends on their phosphorylation, and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), a known negative regulator of Hedgehog signaling serves as a responsible kinase. A Gli2 mutant engineered to eliminate this interaction exhibited increased transcriptional activity (2 approximately 3x). Transcriptional repression by 14-3-3 binding was also observed with Gli3, when its N-terminal repressor domain was deleted. The phosphorylation sites responsible for the binding to 14-3-3 are distinct from those required for proteolysis, the known mechanism for PKA-induced repression of Hh signaling. Our data propose a novel mechanism in which PKA down-regulates Hedgehog signaling by promoting the interaction between Gli and 14-3-3 as well as proteolysis. Given the certain neuronal or malignant disorders in human caused by the abnormality of 17p13 encompassing 14-3-3epsilon overlap with increased Hh signaling, the Gli-14-3-3 interaction may have pathological significance for those human diseases.
Figures
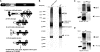
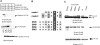



References
-
- Hooper J. E., Scott M. P. (2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 306–317 - PubMed
-
- Taipale J., Beachy P. A. (2001) Nature 411, 349–354 - PubMed
-
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Sánchez P., Dahmane N. (2002) Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 361–372 - PubMed
-
- Pasca di Magliano M., Hebrok M. (2003) Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 903–911 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

