Gli2 trafficking links Hedgehog-dependent activation of Smoothened in the primary cilium to transcriptional activation in the nucleus
- PMID: 19996169
- PMCID: PMC2790365
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912180106
Gli2 trafficking links Hedgehog-dependent activation of Smoothened in the primary cilium to transcriptional activation in the nucleus
Abstract
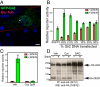
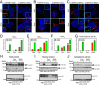
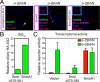
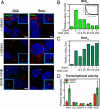
Stimulation by the extracellular Hedgehog (Hh) protein signal has been shown to alter ciliary localization of the mammalian Hh receptor components Smoothened (Smo) and Patched (Ptc), and mutations that disrupt the structure and function of the cilium also disrupt Hh-induced changes in gene expression. But how ciliary events affect gene expression in the nucleus is not known, and to address this question we have characterized the cellular trafficking of Gli2, the principal mediator of Hh-dependent transcriptional activation. From a combination of pharmacological and genetic manipulations we find in resting cells that both Gli2 and Smo appear to shuttle in and out of the cilium, with Gli2 but not Smo requiring intact cytoplasmic microtubules for ciliary entry and both requiring the ciliary retrograde motor, cytoplasmic dynein 2, for ciliary exit. We also find that changes in ciliary and nuclear trafficking of Gli2 are triggered by the Hh-dependent accumulation of activated Smo in the cilium, resulting in a shift from primarily cytoplasmic localization to accumulation at the distal tip of the cilium and within the nucleus. Gli2 thus functions as a dynamic monitor of Smo activity in the cilium and thereby links Hh pathway activation in the cilium to transcriptional activation in the nucleus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chiang C, et al. Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature. 1996;383:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980;287:795–801. - PubMed
-
- Jessell TM. Neuronal specification in the spinal cord: Inductive signals and transcriptional codes. Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–3087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

