Deep sequencing analysis of the Methanosarcina mazei Gö1 transcriptome in response to nitrogen availability
- PMID: 19996181
- PMCID: PMC2799843
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909051106
Deep sequencing analysis of the Methanosarcina mazei Gö1 transcriptome in response to nitrogen availability
Abstract
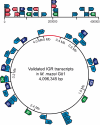
Methanosarcina mazei and related mesophilic archaea are the only organisms fermenting acetate, methylamines, and methanol to methane and carbon dioxide, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas production. The biochemistry of these metabolic processes is well studied, and genome sequences are available, yet little is known about the overall transcriptional organization and the noncoding regions representing 25% of the 4.01-Mb genome of M. mazei. We present a genome-wide analysis of transcription start sites (TSS) in M. mazei grown under different nitrogen availabilities. Pyrosequencing-based differential analysis of primary vs. processed 5' ends of transcripts discovered 876 TSS across the M. mazei genome. Unlike in other archaea, in which leaderless mRNAs are prevalent, the majority of the detected mRNAs in M. mazei carry long untranslated 5' regions. Our experimental data predict a total of 208 small RNA (sRNA) candidates, mostly from intergenic regions but also antisense to 5' and 3' regions of mRNAs. In addition, 40 new small mRNAs with ORFs of < or = 30 aa were identified, some of which might have dual functions as mRNA and regulatory sRNA. We confirmed differential expression of several sRNA genes in response to nitrogen availability. Inspection of their promoter regions revealed a unique conserved sequence motif associated with nitrogen-responsive regulation, which might serve as a regulator binding site upstream of the common IIB recognition element. Strikingly, several sRNAs antisense to mRNAs encoding transposases indicate nitrogen-dependent transposition events. This global TSS map in archaea will facilitate a better understanding of transcriptional and posttranscriptional control in the third domain of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
sRNA154 a newly identified regulator of nitrogen fixation in Methanosarcina mazei strain Gö1.RNA Biol. 2017 Nov 2;14(11):1544-1558. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1306170. Epub 2017 Apr 27. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28296572 Free PMC article.
-
Global transcriptional analysis of Methanosarcina mazei strain Gö1 under different nitrogen availabilities.Mol Genet Genomics. 2006 Jul;276(1):41-55. doi: 10.1007/s00438-006-0117-9. Epub 2006 Apr 20. Mol Genet Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16625354
-
The genome of Methanosarcina mazei: evidence for lateral gene transfer between bacteria and archaea.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 Jul;4(4):453-61. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 12125824
-
The molecular basis of salt adaptation in Methanosarcina mazei Gö1.Arch Microbiol. 2008 Sep;190(3):271-9. doi: 10.1007/s00203-008-0363-9. Epub 2008 Apr 1. Arch Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18379758 Review.
-
Small regulatory RNAs in Archaea.RNA Biol. 2014;11(5):484-93. doi: 10.4161/rna.28452. Epub 2014 Mar 31. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24755959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Archaeal Translation Initiation.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 18;11:584152. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.584152. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33072057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global mapping transcriptional start sites revealed both transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of cold adaptation in the methanogenic archaeon Methanolobus psychrophilus.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 18;5:9209. doi: 10.1038/srep09209. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25784521 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of improved differential and global RNA-seq reveals pervasive transcription initiation and events in all stages of the life-cycle of functional RNAs in Propionibacterium acnes, a major contributor to wide-spread human disease.BMC Genomics. 2013 Sep 14;14:620. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-620. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24034785 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of CRISPR and riboswitch related RNAs among novel noncoding RNAs of the euryarchaeon Pyrococcus abyssi.BMC Genomics. 2011 Jun 13;12:312. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-312. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21668986 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing a markerless genetic exchange system for Methanosarcina mazei strain Gö1 for constructing chromosomal mutants of small RNA genes.Archaea. 2011;2011:439608. doi: 10.1155/2011/439608. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Archaea. 2011. PMID: 21941461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rogers JE, Whitman WB, editors. Microbial Production and Consumption of Greenhouse Gases: Methane, Nitrogen Oxides and Halomethanes. Washington, DC: ASM; 1991.
-
- Deppenmeier U, et al. The genome of Methanosarcina mazei: Evidence for lateral gene transfer between bacteria and archaea. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002;4:453–461. - PubMed
-
- Ferry JG. Enzymology of one-carbon metabolism in methanogenic pathways. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1999;23:13–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

