Smoking-Related Gene Expression in Laser Capture-Microdissected Human Lung
- PMID: 19996203
- PMCID: PMC4238890
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1694
Smoking-Related Gene Expression in Laser Capture-Microdissected Human Lung
Abstract
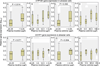
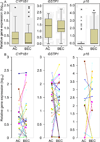
PURPOSE: Interindividual differences in quantitative expression could underlie a propensity for lung cancer. To determine precise individual gene expression signatures on a lung compartment-specific basis, we investigated the expression of carcinogen metabolism genes encoding cytochromes P450 (CYP) 1B1, 2A13, GSTP1, and a tumor suppressor gene p16 in laser capture-microdissected samples of human alveolar compartment (AC) and bronchial epithelial compartment (BEC) lung tissue from 62 smokers and nonsmokers. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Tobacco exposure was determined by plasma nicotine, cotinine, and smoking history. Precise mRNA expression was determined using our RNA-specific qRT-PCR strategy, and correlated with detailed demographic and clinical characteristics. RESULTS: Several correlations of mRNA expression included (a) CYP1B1 in AC (positively with plasma nicotine level, P = 0.008; plasma cotinine level, P = 0.001), (b) GSTP1 in AC (positively with plasma cotinine level, P = 0.003), and (c) GSTP1 in BEC (negatively with smoke dose, P = 0.043; occupational risk, P = 0.019). CYP2A13 was rarely expressed in AC and not expressed in BEC. p16 expression was not correlated with any measured factor. For each gene, subjects showed expression that was individually concordant between these compartments. No clear association of mRNA expression with lung cancer risk was observed in this pilot analysis. CONCLUSIONS: The association between lung mRNA expression and tobacco exposure implies that gene-tobacco interaction is a measurable quantitative trait, albeit with wide interindividual variation. Gene expression tends to be concordant for alveolar and bronchial compartments for these genes in an individual, controlling for proximate tobacco exposure. (Clin Cancer Res 2009;15(24):7562-70).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantitative RT-PCR measurement of cytochromes p450 1A1, 1B1, and 2B7, microsomal epoxide hydrolase, and NADPH oxidoreductase expression in lung cells of smokers and nonsmokers.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997 Jul;17(1):114-24. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.17.1.2783. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9224217
-
Phase I and II carcinogen metabolism gene expression in human lung tissue and tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Dec 1;9(16 Pt 1):6002-11. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14676126 Clinical Trial.
-
Gene-environment interaction signatures by quantitative mRNA profiling in exfoliated buccal mucosal cells.Cancer Res. 2004 Sep 15;64(18):6805-13. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1771. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15375000
-
Biochemistry of nicotine metabolism and its relevance to lung cancer.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100722. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100722. Epub 2021 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33932402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of exposure to gaseous and particulate phase components of tobacco smoke in active and passive smokers.Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1990;62(6):459-66. doi: 10.1007/BF00379064. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1990. PMID: 2246065 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome Wide Methylome Alterations in Lung Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 18;10(12):e0143826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143826. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26683690 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate dietary phytochemicals modulate expression of phase II enzymes GSTP1 and NQO1 in human lung cells.J Nutr. 2010 Aug;140(8):1404-10. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.121905. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20554899 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen metabolism within the lung and its modulation by tobacco smoke.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Apr;34(4):909-15. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs402. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23276798 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the transcriptome in molecular epidemiology studies.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2013 Aug;54(7):500-17. doi: 10.1002/em.21798. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2013. PMID: 23907930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput library screening identifies two novel NQO1 inducers in human lung cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Mar;46(3):365-71. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0301OC. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22021338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lacroix L, Commo F, Soria JC. Gene expression profiling of non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008;8:167–178. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

