Emerging roles of the EBF family of transcription factors in tumor suppression
- PMID: 19996307
- PMCID: PMC5545892
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0229
Emerging roles of the EBF family of transcription factors in tumor suppression
Abstract
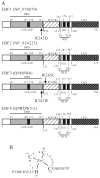
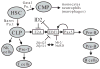
Alterations in various developmental pathways are common themes in cancer. The early B-cell factors (EBF) are a family of four highly conserved DNA-binding transcription factors with an atypical zinc-finger and helix-loop-helix motif. They are involved in the differentiation and maturation of several cell lineages including B-progenitor lymphoblasts, neuronal precursors, and osteoblast progenitors. During B-cell development, EBF1 is required for the expression of Pax5, an essential factor for the production of antibody-secreting cells. Accumulating evidence indicates that genomic deletion of the EBF1 gene contributes to the pathogenesis, drug resistance, and relapse of B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Epigenetic silencing and genomic deletion of the EBF3 locus in chromosome 10q are very frequent in glioblastoma (GBM). Strikingly, the frequency of EBF3 loss in GBM is similar to that of the loss of Pten, a key suppressor of gliomagenesis. Cancer-specific somatic mutations were detected in EBF3 in GBM and in both EBF1 and EBF3 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. These missense mutations occur in the DNA-binding domain or the conserved IPT/TIG domain, suggesting that they might disrupt the functions of these two proteins. Functional studies revealed that EBF3 represses the expression of genes required for cell proliferation [e.g., cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK)] and survival (e.g., Mcl-1 and Daxx) but activates those involved in cell cycle arrest (e.g., p21 and p27), leading to growth suppression and apoptosis. Therefore, EBFs represent new tumor suppressors whose inactivation blocks normal development and contributes to tumorigenesis of diverse types of human cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, et al. The genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2007;318:1108–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

