Insulin induces REDD1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation in adipocytes
- PMID: 19996311
- PMCID: PMC2820742
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.047688
Insulin induces REDD1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation in adipocytes
Abstract
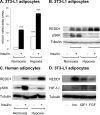
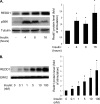
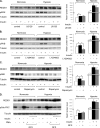
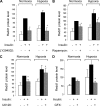
REDD1 (regulated in development and DNA damage responses) is essential for the inhibition of mTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex) signaling pathway in response to hypoxia. REDD1 expression is regulated by many stresses such as hypoxia, oxidative stress, and energy depletion. However, the regulation of REDD1 expression in response to insulin remains unknown. In the present study, we demonstrate that in murine and in human adipocytes, insulin stimulates REDD1 expression. Insulin-induced REDD1 expression occurs through phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mTOR-dependent pathways. Moreover, using echinomycin, a hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) inhibitor, and HIF-1alpha small interfering RNA, we demonstrate that insulin stimulates REDD1 expression only through the transcription factor HIF-1. In conclusion, our study shows that insulin stimulates REDD1 expression in adipocytes.
Figures
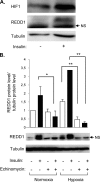
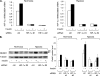
Similar articles
-
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, regulated in development and DNA damage response-1 and mammalian target of rapamycin in human placental BeWo cells under hypoxia.Placenta. 2016 Sep;45:24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Placenta. 2016. PMID: 27577706
-
Regulated in development and DNA damage responses -1 (REDD1) protein contributes to insulin signaling pathway in adipocytes.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052154. Epub 2012 Dec 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23272222 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic condition- and high cell density-induced expression of Redd1 is regulated by activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and Sp1 through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.Cell Signal. 2007 Jul;19(7):1393-403. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.12.014. Epub 2007 Jan 20. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17307335
-
The stress-responsive protein REDD1 and its pathophysiological functions.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Sep;55(9):1933-1944. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01056-3. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37653030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional Sensor REDD1 in Cancer and Inflammation: Friend or Foe?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 26;23(17):9686. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179686. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077083 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
REDD1 promotes obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction via atypical NF-κB activation.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 22;13(1):6303. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34110-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36272977 Free PMC article.
-
Quinolinic acid induces cell apoptosis in PC12 cells through HIF-1-dependent RTP801 activation.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Apr;31(2):435-44. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9782-x. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 26738727
-
DDiT4L promotes autophagy and inhibits pathological cardiac hypertrophy in response to stress.Sci Signal. 2017 Feb 28;10(468):eaaf5967. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf5967. Sci Signal. 2017. PMID: 28246202 Free PMC article.
-
Altered nutrient response of mTORC1 as a result of changes in REDD1 expression: effect of obesity vs. REDD1 deficiency.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Aug 1;117(3):246-56. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01350.2013. Epub 2014 May 29. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 24876363 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide B Protects Neurons from Ischemic Injury by Inhibiting the Expression of RTP801.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Oct;35(7):943-52. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0189-3. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25869596 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

