Mammalian Tribbles homolog 3 impairs insulin action in skeletal muscle: role in glucose-induced insulin resistance
- PMID: 19996382
- PMCID: PMC2838520
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00467.2009
Mammalian Tribbles homolog 3 impairs insulin action in skeletal muscle: role in glucose-induced insulin resistance
Abstract
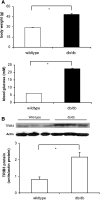
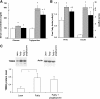
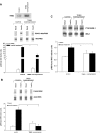
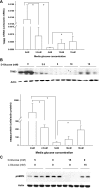
Tribbles homolog 3 (TRIB3) was found to inhibit insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation and modulate gluconeogenesis in rodent liver. Currently, we examined a role for TRIB3 in skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Ten insulin-sensitive, ten insulin-resistant, and ten untreated type 2 diabetic (T2DM) patients were metabolically characterized by hyperinsulinemic euglycemic glucose clamps, and biopsies of vastus lateralis were obtained. Skeletal muscle samples were also collected from rodent models including streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats, db/db mice, and Zucker fatty rats. Finally, L6 muscle cells were used to examine regulation of TRIB3 by glucose, and stable cell lines hyperexpressing TRIB3 were generated to identify mechanisms underlying TRIB3-induced insulin resistance. We found that 1) skeletal muscle TRIB3 protein levels are significantly elevated in T2DM patients; 2) muscle TRIB3 protein content is inversely correlated with glucose disposal rates and positively correlated with fasting glucose; 3) skeletal muscle TRIB3 protein levels are increased in STZ-diabetic rats, db/db mice, and Zucker fatty rats; 4) stable TRIB3 hyperexpression in muscle cells blocks insulin-stimulated glucose transport and glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation and impairs phosphorylation of Akt, ERK, and insulin receptor substrate-1 in insulin signal transduction; and 5) TRIB3 mRNA and protein levels are increased by high glucose concentrations, as well as by glucose deprivation in muscle cells. These data identify TRIB3 induction as a novel molecular mechanism in human insulin resistance and diabetes. TRIB3 acts as a nutrient sensor and could mediate the component of insulin resistance attributable to hyperglycemia (i.e., glucose toxicity) in diabetes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of TRIB3 in regulation of insulin sensitivity and nutrient metabolism during short-term fasting and nutrient excess.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Oct 1;303(7):E908-16. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00663.2011. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22850683 Free PMC article.
-
TRIB3 mediates glucose-induced insulin resistance via a mechanism that requires the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway.Diabetes. 2013 Dec;62(12):4192-200. doi: 10.2337/db13-0312. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23990361 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal Muscle TRIB3 Mediates Glucose Toxicity in Diabetes and High- Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance.Diabetes. 2016 Aug;65(8):2380-91. doi: 10.2337/db16-0154. Epub 2016 May 10. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27207527 Free PMC article.
-
The mammalian tribbles homolog TRIB3, glucose homeostasis, and cardiovascular diseases.Endocr Rev. 2012 Aug;33(4):526-46. doi: 10.1210/er.2011-1042. Epub 2012 May 10. Endocr Rev. 2012. PMID: 22577090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
Cited by
-
Variants of insulin-signaling inhibitor genes in type 2 diabetes and related metabolic abnormalities.Int J Genomics. 2013;2013:376454. doi: 10.1155/2013/376454. Epub 2013 May 23. Int J Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23762820 Free PMC article.
-
TRIB3 Mediates Fibroblast Activation and Fibrosis though Interaction with ATF4 in IPF.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 11;23(24):15705. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415705. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555349 Free PMC article.
-
Tribbles Homolog 3 Promotes Foam Cell Formation Associated with Decreased Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Macrophages: Evidence for Reciprocal Regulation of Cholesterol Uptake and Inflammation.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2016 Feb;14(1):7-15. doi: 10.1089/met.2015.0037. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 26584255 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome expression profile in neuroblastoma cells exposed to 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine.Neurotoxicology. 2012 Oct;33(5):1156-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Neurotoxicology. 2012. PMID: 22776087 Free PMC article.
-
Association of TRB3 Q84R polymorphism with polycystic ovary syndrome in Chinese women.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011 Apr 14;9:46. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-9-46. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21492415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreozzi F, Formoso G, Prudente S, Hribal ML, Pandolfi A, Bellacchio E, Di Silvestre S, Trischitta V, Consoli A, Sesti G. TRIB3 R84 variant is associated with impaired insulin-mediated nitric oxide production in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28: 1355–1360, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay GK, Yu JG, Ofrecio J, Olefsky JM. Increased p85/55/50 expression and decreased phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase activity in insulin-resistant human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 54: 2351–2359, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bi XP, Tan HW, Xing SS, Wang ZH, Tang MX, Zhang Y, Zhang W. Overexpression of TRB3 gene in adipose tissue of rats with high fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Endocr J 55: 747–752, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bowers AJ, Scully S, Boylan JF. SKIP3, a novel Drosophila tribbles ortholog, is overexpressed in human tumors and is regulated by hypoxia. Oncogene 22: 2823–2835, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

