The human "Treg MLR": immune monitoring for FOXP3+ T regulatory cell generation
- PMID: 19996930
- PMCID: PMC2792565
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181bbee98
The human "Treg MLR": immune monitoring for FOXP3+ T regulatory cell generation
Abstract
Background: Controversy exists about the conditions effecting the development of forkhead/winghead helix transcription factor P3 (FOXP3) expressing T cells and their relevance in transplant recipients.
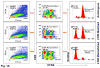
Methods: We generated carboxy-fluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester-labeled CD4+CD25 high FOXP3+ cells in mixed lymphocyte reactions (MLRs) ("the Treg MLR"), with varying human leukocyte antigen (HLA) disparities and cell components. Five color flow cytometry and H-thymidine uptakes were the readouts.
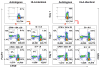
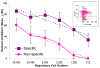
Results: (1) Despite lower stimulation indices (SIs) than two DR-mismatched MLRs, 2 DR-matched MLRs generated more than twofold higher percentages when gating on proliferating CD4+CD25 high FOXP3+ cells; (2) Even with low numbers of proliferating cells, autologous and HLA identical MLRs generated the highest FOXP3+:FOXP3- cell ratios; (3) Elimination of either non-CD3+ responding cells (resulting in "direct presentation" only) or responding CD25+ (Treg generating) cells increased the SI but inhibited proliferating CD4+CD25 high FOXP3+ cell development; (4) MLR-generated CD4+CD25 high FOXP3+ cells added as third components specifically inhibited the same freshly set MLR SI and caused recruitment of new CD4+CD25 high FOXP3+ cells. As an example of the "Treg MLR" immune monitoring potential, addition of third component peripheral blood mononuclear cell containing high percentages of CD4+CD25 high FOXP3+ cells from an HLA identical kidney transplant recipient (in a tolerance protocol) caused donor-specific Treg MLR inhibition or recruitment. This was similar to the third component MLR Tregs generated entirely in vitro.
Conclusion: In the Treg MLR, the generation of CD4+CD25 high FOXP3+ cells is more pronounced in the context of self-recognition (HLA matching, indirect presentation). These cells can be assayed for MLR inhibitory and Treg recruitment functions, so as to immunologically monitor the allospecific regulation after transplantation.
Figures



References
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(4):345. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Migliavacca B, Horejs-Hoeck J, Kaupper T, Roncarolo MG. Rapamycin promotes expansion of functional CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells of both healthy subjects and type 1 diabetic patients. J Immunol. 2006;177(12):8338. - PubMed
-
- Fathman CG, Collavo D, Davies S, Nabholz M. In vitro secondary MLR. I. Kinetics of proliferation and specificity of in vitro primed responder cells. J Immunol. 1977;118(4):1232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

