Addition of extended zidovudine to extended nevirapine prophylaxis reduces nevirapine resistance in infants who were HIV-infected in utero
- PMID: 19996936
- PMCID: PMC3063063
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283352ef1
Addition of extended zidovudine to extended nevirapine prophylaxis reduces nevirapine resistance in infants who were HIV-infected in utero
Abstract
Background: In the Post-Exposure Prophylaxis of Infants (PEPI)-Malawi trial, most women received single-dose nevirapine (NVP) at delivery, and infants in the extended study arms received single-dose NVP along with 1 week of daily zidovudine (ZDV), followed by either extended daily NVP or extended daily NVP and ZDV up to 14 weeks of age. Although extended NVP prophylaxis reduces the risk of postnatal HIV transmission, it may increase the risk of NVP resistance among infants who are HIV-infected despite prophylaxis.
Methods: We analyzed 88 infants in the PEPI-Malawi trial who were HIV-infected in utero and who received prophylaxis for a median of 6 weeks prior to HIV diagnosis. HIV genotyping was performed using the ViroSeq HIV Genotyping System.
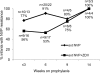
Results: At 14 weeks of age, the proportion of infants with NVP resistance was lower in the extended NVP and ZDV arm than in the extended NVP arm (28/45, 62.2% vs. 37/43, 86.0%; P = 0.015). None of the infants had ZDV resistance. Addition of extended ZDV to extended NVP was associated with reduced risk of NVP resistance at 14 weeks if prophylaxis was stopped by 6 weeks (54.5 vs. 85.7%, P = 0.007) but not if prophylaxis was continued beyond 6 weeks (83.3 vs. 87.5%, P = 1.00).
Conclusion: Addition of extended ZDV to extended NVP prophylaxis significantly reduced the risk of NVP resistance at 14 weeks in infants who were HIV-infected in utero, provided that HIV infection was diagnosed and the prophylaxis was stopped by 6 weeks of age.
Figures
References
-
- Bedri A, Gudetta B, Isehak A, et al. Extended-dose nevirapine to 6 weeks of age for infants to prevent HIV transmission via breastfeeding in Ethiopia, India, and Uganda: an analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2008;372:300–13. - PubMed
-
- Kumwenda NI, Hoover DR, Mofenson LM, et al. Extended antiretroviral prophylaxis to reduce breast-milk HIV-1 transmission. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:119–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

