Monte Carlo simulation of photon migration in 3D turbid media accelerated by graphics processing units
- PMID: 19997242
- PMCID: PMC2863034
- DOI: 10.1364/OE.17.020178
Monte Carlo simulation of photon migration in 3D turbid media accelerated by graphics processing units
Abstract
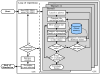
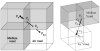
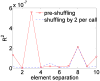
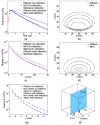
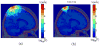
We report a parallel Monte Carlo algorithm accelerated by graphics processing units (GPU) for modeling time-resolved photon migration in arbitrary 3D turbid media. By taking advantage of the massively parallel threads and low-memory latency, this algorithm allows many photons to be simulated simultaneously in a GPU. To further improve the computational efficiency, we explored two parallel random number generators (RNG), including a floating-point-only RNG based on a chaotic lattice. An efficient scheme for boundary reflection was implemented, along with the functions for time-resolved imaging. For a homogeneous semi-infinite medium, good agreement was observed between the simulation output and the analytical solution from the diffusion theory. The code was implemented with CUDA programming language, and benchmarked under various parameters, such as thread number, selection of RNG and memory access pattern. With a low-cost graphics card, this algorithm has demonstrated an acceleration ratio above 300 when using 1792 parallel threads over conventional CPU computation. The acceleration ratio drops to 75 when using atomic operations. These results render the GPU-based Monte Carlo simulation a practical solution for data analysis in a wide range of diffuse optical imaging applications, such as human brain or small-animal imaging.
Figures

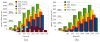
References
-
- Rubinstein RY, Kroese DP. Simulation and the Monte Carlo Method. 2nd. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 2007.
-
- Wang LH, Jacques SL, Zheng LQ. MCML Monte Carlo modeling of light transport in multilayered tissues. Comput Meth Prog Bio. 1995;47(2):131–146. - PubMed
-
- Hiraoka M, Firbank M, Essenpreis M, Cope M, Arridge SR, van der Zee P, Delpy DT. A Monte Carlo investigation of optical pathlength in inhomogeneous tissue and its application to near-infrared spectroscopy. Phys Med Biol. 1993;38(12):1859–1876. - PubMed
-
- Boas DA, Culver JP, Stott JJ, Dunn AK. Three dimensional Monte Carlo code for photon migration through complex heterogeneous media including the adult human head. Opt Express. 2002;10(3):159–170. - PubMed
-
- Tuchin VV, editor. Handbook of Optical Biomedical Diagnostics, SPIE Press Monograph. 2002;PM107
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

