A pilot study of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) overexpression in the brush cytology of patients with malignant pancreatic or biliary strictures
- PMID: 19997513
- PMCID: PMC2786994
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/805971
A pilot study of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) overexpression in the brush cytology of patients with malignant pancreatic or biliary strictures
Abstract
We have previously demonstrated that uPA is overexpressed in pancreatic tumors. In an attempt to diagnose these tumors earlier, we sought to determine whether uPA could be identified in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography obtained brushings in patients with malignant pancreatic and biliary strictures. Secondarily, uPA was measured in the serum of this patient population. uPA overexpression was identified in the cytologic tissue in 8 of 11 patients (72.7%). Serum analysis demonstrated a 2-fold higher concentration of uPA in the pancreaticobiliary cancer patients (1.27 versus 0.56 ng/mL; P = .0182). Also, uPA overexpression correlated with serum levels (P < .0001). This study confirms that uPA can be detected in the ERCP cytologically obtained tissue and is frequently present in a higher concentration in the serum of pancreaticobiliary cancer patients. A larger sample size will be required to address its value as a sensitive marker for the diagnosis of pancreatic or biliary cancers.
Figures
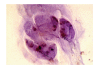
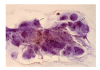
Similar articles
-
In situ hybridization for telomerase RNA in routine cytologic brushings for the diagnosis of pancreaticobiliary malignancies.Gastrointest Endosc. 1998 Oct;48(4):402-5. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(98)70011-2. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. PMID: 9786114
-
Brush cytology of ductal strictures during ERCP.Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2000 Jul-Sep;63(3):254-9. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2000. PMID: 11189981
-
Brush cytology during ERCP for the diagnosis of biliary and pancreatic malignancies.Gastrointest Endosc. 1994 Mar-Apr;40(2 Pt 1):140-5. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(94)70155-5. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994. PMID: 8013810
-
Sensitivity of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography standard cytology: 10-y review of the literature.J Surg Res. 2013 Sep;184(1):304-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.06.028. Epub 2013 Jul 5. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23866788 Review.
-
Value of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography-guided brushings in preoperative assessment of pancreaticobiliary strictures: what's new?Acta Cytol. 2008 Jan-Feb;52(1):24-34. doi: 10.1159/000325431. Acta Cytol. 2008. PMID: 18323272 Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant Factors of Fibrinolysis and Coagulation in Pancreatic Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Jan 6;14:53-65. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S281251. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33442266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimal tissue sampling during ERCP and emerging molecular techniques for the differentiation of benign and malignant biliary strictures.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 15;14:17562848211002023. doi: 10.1177/17562848211002023. eCollection 2021. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33948111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional roles of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) in cancer stemness and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Sep;24(17):2620-32. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-04-0306. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23864708 Free PMC article.
-
Serum levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in healthy dogs and oncologic canine patients.Vet World. 2017 Aug;10(8):918-923. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.918-923. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Vet World. 2017. PMID: 28919683 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and validation of a nomogram based on coagulation parameters to predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 15;23(1):548. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10908-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37322417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcea G, Neal CP, Pattenden CJ, Steward WP, Berry DP. Molecular prognostic markers in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review. European Journal of Cancer. 2005;41(15):2213–2236. - PubMed
-
- Duffy MJ. Proteases as prognostic markers in cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 1996;2(4):613–618. - PubMed
-
- Livant DL. Targeting invasion induction as a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of cancer. Current Cancer Drug Targets. 2005;5(7):489–503. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen PA, Kjoller L, Christensen L, Duffy MJ. The urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in cancer metastasis: a review. International Journal of Cancer. 1997;72(1):1–22. - PubMed
-
- Look MP, van Putten WLJ, Duffy MJ, et al. Pooled analysis of prognostic impact of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor PAI-1 in 8377 breast cancer patients. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2002;94(2):116–128. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

