Long-term trend in the incidence of acute myocardial infarction in Korea: 1997-2007
- PMID: 19997542
- PMCID: PMC2790125
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2009.39.11.467
Long-term trend in the incidence of acute myocardial infarction in Korea: 1997-2007
Abstract
Background and objectives: Information about disease incidence is indispensable for the active prevention and control of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). The purpose of this study was to provide basic information for the establishment of policy related to AMI by examining the long-term trends in incidence of AMI.
Subjects and methods: This study identified the trend in disease incidence during between 1997 and 2007 using the Korean National Health Insurance Database that includes AMI {the 10th International Classification of Disease (ICD-10) code: I21, I22, I23, I250, I251} as a primary or secondary disease.
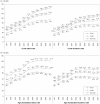
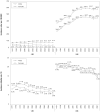
Results: The attack and incidence rates for AMI in 2007 were 118.4 and 91.8 per 100,000 persons, respectively, and the rates more than doubled for the 11 years. Both rates were higher among males than females and increased more in the older age groups. Incidence cases accounted for most of the total attack cases every year; however, in recent years the proportion of relapse cases was on the rise. The case fatality rate was highest (14.5%) in 2000, and declined rapidly to 9.8% in 2007. The case fatality rate was higher among females than males and the older age groups; in particular, female patients >/=65 years of age had the highest fatality rate.
Conclusion: This study showed that AMI has been on the rise in Korea for 11 years. Therefore, the establishment of policy for intensive control of the incidence of AMI is necessary by building a continuous monitoring and surveillance system.
Keywords: Mortality; Myocardial infarction; Prognosis.
Figures
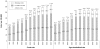

Similar articles
-
Long-term trends in the incidence, treatment, hospital fatality and subsequent mortality from acute myocardial infarction in the Czech Republic.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2021 Sep;165(3):283-290. doi: 10.5507/bp.2020.014. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2021. PMID: 32285848
-
Incidence and case fatality of acute myocardial infarction in Korea, 2011-2020.Epidemiol Health. 2024;46:e2024002. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2024002. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Epidemiol Health. 2024. PMID: 38186244 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence, treatment, in-hospital mortality and one-year outcomes of acute myocardial infarction in Poland in 2009-2012--nationwide AMI-PL database.Kardiol Pol. 2015;73(3):142-58. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2014.0213. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Kardiol Pol. 2015. PMID: 25371307
-
A two-decades (1975 to 1995) long experience in the incidence, in-hospital and long-term case-fatality rates of acute myocardial infarction: a community-wide perspective.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 May;33(6):1533-9. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00040-6. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999. PMID: 10334419
-
The Trend in Incidence and Case-fatality of Hospitalized Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients in Korea, 2007 to 2016.J Korean Med Sci. 2019 Dec 30;34(50):e322. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e322. J Korean Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31880418 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Treatment of acute myocardial infarction in the sub-arctic region of Norway. Do we offer an equal quality of care?Int J Circumpolar Health. 2017;76(1):1391651. doi: 10.1080/22423982.2017.1391651. Int J Circumpolar Health. 2017. PMID: 29069984 Free PMC article.
-
Recent trends in economic burden of acute myocardial infarction in South Korea.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0117446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117446. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25658119 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Incidence and Case Fatality Rates of Heart Disease and Its Subtypes in Korea, 2006-2015.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 15;17(22):8451. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228451. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33203087 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and Disparities of Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stroke in Korea, 2008-2019.Yonsei Med J. 2024 Sep;65(9):534-543. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0570. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 39193762 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of noncommunicable diseases and national strategies to control them in Korea.J Prev Med Public Health. 2013 Jul;46(4):155-64. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.2013.46.4.155. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Prev Med Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23946873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyun DW, Kim KS, Synn YC, et al. Clinical characteristic of acute infarction died during hospitalization. Korean Circ J. 1998;28:1518–1526.
-
- Tunstall-Pedoe H, Kuulasmaa K, Amouyel P, Arveiler D, Rajakangas AM, Pajak A. Myocardial infarction and coronary deaths in the World Health Organization MONICA Project: registration procedures, event rates, and case-fatality rates in 38 populations from 21 countries in four continents. Circulation. 1994;90:583–612. - PubMed
-
- Fortmann SP, Haskell WL, Williams PT, Varady AN, Hulley SB, Farquhar JW. Community surveillance of cardiovascular diseases in the Stanford Five-City Project: methods and initial experience. Am J Epidemiol. 1986;123:656–669. - PubMed
-
- Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, Bassand JP. Myocardial infarction redefined: a consensus document of The Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:959–969. - PubMed
-
- Kim JY. Construction of National Surveillance System for Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease. Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service; 2006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

