P-glycoprotein acts as an immunomodulator during neuroinflammation
- PMID: 19997559
- PMCID: PMC2785479
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008212
P-glycoprotein acts as an immunomodulator during neuroinflammation
Abstract
Background: Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system in which autoreactive myelin-specific T cells cause extensive tissue damage, resulting in neurological deficits. In the disease process, T cells are primed in the periphery by antigen presenting dendritic cells (DCs). DCs are considered to be crucial regulators of specific immune responses and molecules or proteins that regulate DC function are therefore under extensive investigation. We here investigated the potential immunomodulatory capacity of the ATP binding cassette transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp). P-gp generally drives cellular efflux of a variety of compounds and is thought to be involved in excretion of inflammatory agents from immune cells, like DCs. So far, the immunomodulatory role of these ABC transporters is unknown.
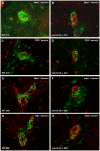
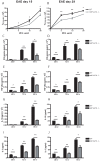
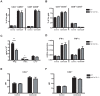
Methods and findings: Here we demonstrate that P-gp acts as a key modulator of adaptive immunity during an in vivo model for neuroinflammation. The function of the DC is severely impaired in P-gp knockout mice (Mdr1a/1b-/-), since both DC maturation and T cell stimulatory capacity is significantly decreased. Consequently, Mdr1a/1b -/- mice develop decreased clinical signs of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model for multiple sclerosis. Reduced clinical signs coincided with impaired T cell responses and T cell-specific brain inflammation. We here describe the underlying molecular mechanism and demonstrate that P-gp is crucial for the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma. Importantly, the defect in DC function can be restored by exogenous addition of these cytokines.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that P-gp downmodulates DC function through the regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion, resulting in an impaired immune response. Taken together, our work highlights a new physiological role for P-gp as an immunomodulatory molecule and reveals a possible new target for immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
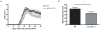

Similar articles
-
Dendritic cells phenotype fitting under hypoxia or lipopolysaccharide; adenosine 5'-triphosphate-binding cassette transporters far beyond an efflux pump.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Jun;172(3):444-54. doi: 10.1111/cei.12067. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23600833 Free PMC article.
-
The type IV phosphodiesterase specific inhibitor mesopram inhibits experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rodents.J Neuroimmunol. 2000 Aug 1;108(1-2):136-46. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(00)00265-4. J Neuroimmunol. 2000. PMID: 10900347
-
Inhibitory role of CD19 in the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating cytokine response.Am J Pathol. 2006 Mar;168(3):812-21. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050923. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16507897 Free PMC article.
-
The porcine dendritic cell family.Dev Comp Immunol. 2009 Mar;33(3):299-309. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18582937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P-glycoprotein--a novel therapeutic target for immunomodulation in clinical transplantation and autoimmunity?Curr Drug Targets. 2003 Aug;4(6):469-76. doi: 10.2174/1389450033490894. Curr Drug Targets. 2003. PMID: 12866661 Review.
Cited by
-
The human P-glycoprotein transporter enhances the type I interferon response to Listeria monocytogenes infection.Infect Immun. 2015 Jun;83(6):2358-68. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00380-15. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25824830 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of pannexin1 to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 20;8(6):e66657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066657. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23885286 Free PMC article.
-
Perplexing Role of P-Glycoprotein in Tumor Microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 5;10:265. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00265. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32195185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel in vivo regulatory role of P-glycoprotein in alloimmunity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Apr 9;394(3):646-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.040. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20230790 Free PMC article.
-
Expression QTL mapping in regulatory and helper T cells from the BXD family of strains reveals novel cell-specific genes, gene-gene interactions and candidate genes for auto-immune disease.BMC Genomics. 2011 Dec 19;12:610. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-610. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22182475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ewing C, Bernard CC. Insights into the aetiology and pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Immunol Cell Biol. 1998;76:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Frohman EM, Racke MK, Raine CS. Multiple sclerosis–the plaque and its pathogenesis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:942–955. - PubMed
-
- Lassmann H, Bruck W, Lucchinetti C. Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis pathogenesis: implications for diagnosis and therapy. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7:115–121. - PubMed
-
- Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Noseworthy J. Multiple sclerosis: recent developments in neuropathology, pathogenesis, magnetic resonance imaging studies and treatment. Curr Opin Neurol. 2001;14:259–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

