The treatment of diabetic foot infections: focus on ertapenem
- PMID: 19997576
- PMCID: PMC2788600
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s3162
The treatment of diabetic foot infections: focus on ertapenem
Abstract
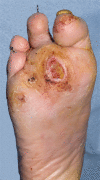
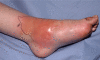
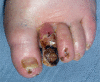
Clinically, 3 distinct stages of diabetic foot infection may be recognized: localized infection, spreading infection and severe infection. Each of these presentations may be complicated by osteomyelitis. Infection can be caused by Gram-positive aerobic, and Gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, singly or in combination. The underlying principles are to diagnose infection, culture the bacteria responsible and treat aggressively with antibiotic therapy. Localized infections with limited cellulitis can generally be treated with oral antibiotics on an outpatient basis. Spreading infection should be treated with systemic antibiotics. Severe deep infections need urgent admission to hospital for wide-spectrum intravenous antibiotics. Clinical and microbiological response rates have been similar in trials of various antibiotics and no single agent or combination has emerged as most effective. Recently, clinical and microbiological outcomes for patients treated with ertapenem were equivalent to those for patients treated with piperacillin/tazobactam. It is also important to judge the need for debridement and surgery, to assess the arterial supply to the foot and consider revascularization either by angioplasty or bypass if the foot is ischemic. It is also important to achieve metabolic control. Thus infection in the diabetic foot needs full multidisciplinary treatment.
Keywords: antibiotics; diabetes; ertapenem; foot; infection.
Figures
References
-
- Pecoraro RE, Reiber GE, Burgess EM. Pathways to diabetic limb amputation. Basis for prevention. Diabetes Care. 1990;13:513–521. - PubMed
-
- Bakker K, Foster AVM, van Houtoum WH, et al.International Diabetes Federation and International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot 2005. Time to Act. The Netherlands.
-
- Reiber GE. Epidemiology of foot ulcers and amputations in the diabetic foot. In: Bowker JH, Pfeifer MA, editors. Levin and O’Neal’s The Diabetic Foot. 6th Ed. Mosby; St. Louis: 2001. pp. 13–32.
-
- Lipsky BA, Berendt AR, Gunner Deery H, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:885–910. - PubMed
-
- Lipsky BA. A report from the international consensus on diagnosing and treating the infected diabetic foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2004;20(Suppl 1):S68–S77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical