Adaptive vaccination strategies to mitigate pandemic influenza: Mexico as a case study
- PMID: 19997603
- PMCID: PMC2781783
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008164
Adaptive vaccination strategies to mitigate pandemic influenza: Mexico as a case study
Abstract
Background: We explore vaccination strategies against pandemic influenza in Mexico using an age-structured transmission model calibrated against local epidemiological data from the Spring 2009 A(H1N1) pandemic.
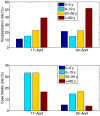
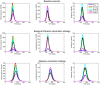
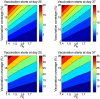
Methods and findings: In the context of limited vaccine supplies, we evaluate age-targeted allocation strategies that either prioritize youngest children and persons over 65 years of age, as for seasonal influenza, or adaptively prioritize age groups based on the age patterns of hospitalization and death monitored in real-time during the early stages of the pandemic. Overall the adaptive vaccination strategy outperformed the seasonal influenza vaccination allocation strategy for a wide range of disease and vaccine coverage parameters.
Conclusions: This modeling approach could inform policies for Mexico and other countries with similar demographic features and vaccine resources issues, with regard to the mitigation of the S-OIV pandemic. We also discuss logistical issues associated with the implementation of adaptive vaccination strategies in the context of past and future influenza pandemics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Update of
-
Adaptive vaccination strategies to mitigate pandemic influenza: Mexico as a case study.PLoS Curr. 2009 Aug 17;1:RRN1004. doi: 10.1371/currents.rrn1004. PLoS Curr. 2009. Update in: PLoS One. 2009 Dec 03;4(12):e8164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008164. PMID: 20025196 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Simonsen L. Pandemic influenza and mortality: past evidence and projections for the future. 2004. pp. 26–46.
-
- Miller MA, Viboud C, Balinska M, Simonsen L. The signature features of influenza pandemics–implications for policy. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2595–2598. - PubMed
-
- Chowell G, Ammon CE, Hengartner NW, Hyman JM. Estimation of the reproductive number of the Spanish flu epidemic in Geneva, Switzerland. Vaccine. 2006;24:6747–6750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

