REST and CoREST modulate neuronal subtype specification, maturation and maintenance
- PMID: 19997604
- PMCID: PMC2782136
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007936
REST and CoREST modulate neuronal subtype specification, maturation and maintenance
Abstract
Background: The repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencer factor (REST/NRSF) is a master regulator of neuronal gene expression. REST functions as a modular scaffold for dynamic recruitment of epigenetic regulatory factors including its primary cofactor, the corepressor for element-1-silencing transcription factor (CoREST), to genomic loci that contain the repressor element-1 (RE1) binding motif. While REST was initially believed to silence RE1 containing neuronal genes in neural stem cells (NSCs) and non-neuronal cells, emerging evidence shows an increasingly complex cell type- and developmental stage-specific repertoire of REST target genes and functions that include regulation of neuronal lineage maturation and plasticity.
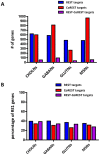
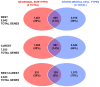
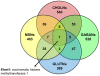
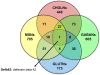
Methodology/principal findings: In this study, we utilized chromatin immunoprecipitation on chip (ChIP-chip) analysis to examine REST and CoREST functions during NSC-mediated specification of cholinergic neurons (CHOLNs), GABAergic neurons (GABANs), glutamatergic neurons (GLUTNs), and medium spiny projection neurons (MSNs). We identified largely distinct but overlapping profiles of REST and CoREST target genes during neuronal subtype specification including a disproportionately high percentage that are exclusive to each neuronal subtype.
Conclusions/significance: Our findings demonstrate that the differential deployment of REST and CoREST is an important regulatory mechanism that mediates neuronal subtype specification by modulating specific gene networks responsible for inducing and maintaining neuronal subtype identity. Our observations also implicate a broad array of factors in the generation of neuronal diversity including but not limited to those that mediate homeostasis, cell cycle dynamics, cell viability, stress responses and epigenetic regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chong JA, Tapia-Ramirez J, Kim S, Toledo-Aral JJ, Zheng Y, et al. REST: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons. Cell. 1995;80:949–957. - PubMed
-
- Schoenherr CJ, Anderson DJ. The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF): a coordinate repressor of multiple neuron-specific genes. Science. 1995;267:1360–1363. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZF, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ. NRSF/REST is required in vivo for repression of multiple neuronal target genes during embryogenesis. Nat Genet. 1998;20:136–142. - PubMed
-
- Brivanlou AH. Should the master regulator Rest in peace? Nat Genet. 1998;20:109–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

