Comprehensive analysis of inflammatory immune mediators in vitreoretinal diseases
- PMID: 19997642
- PMCID: PMC2780733
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008158
Comprehensive analysis of inflammatory immune mediators in vitreoretinal diseases
Abstract
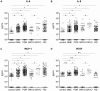
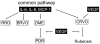
Inflammation affects the formation and the progression of various vitreoretinal diseases. We performed a comprehensive analysis of inflammatory immune mediators in the vitreous fluids from total of 345 patients with diabetic macular edema (DME, n = 92), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR, n = 147), branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO, n = 30), central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO, n = 13) and rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD, n = 63). As a control, we selected a total of 83 patients with either idiopathic macular hole (MH) or idiopathic epiretinal membrane (ERM) that were free of major pathogenic intraocular changes, such as ischemic retina and proliferative membranes. The concentrations of 20 soluble factors (nine cytokines, six chemokines, and five growth factors) were measured simultaneously by multiplex bead analysis system. Out of 20 soluble factors, three factors: interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) were significantly elevated in all groups of vitreoretinal diseases (DME, PDR, BRVO, CRVO, and RRD) compared with control group. According to the correlation analysis in the individual patient's level, these three factors that were simultaneously increased, did not show any independent upregulation in all the examined diseases. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was significantly elevated in patients with PDR and CRVO. In PDR patients, the elevation of VEGF was significantly correlated with the three factors: IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1, while no significant correlation was observed in CRVO patients. In conclusion, multiplex bead system enabled a comprehensive soluble factor analysis in vitreous fluid derived from variety of patients. Major three factors: IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 were strongly correlated with each other indicating a common pathway involved in inflammation process in vitreoretinal diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


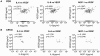
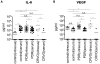
References
-
- Canton A, Martinez-Caceres EM, Hernandez C, Espejo C, Garcia-Arumi J, et al. CD4-CD8 and CD28 expression in T cells infiltrating the vitreous fluid in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy: a flow cytometric analysis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:743–749. - PubMed
-
- Charteris DG, Hiscott P, Grierson I, Lightman SL. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Lymphocytes in epiretinal membranes. Ophthalmology. 1992;99:1364–1367. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheim JJ. Cytokines: past, present, and future. Int J Hematol. 2001;74:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Vilcek J, Feldmann M. Historical review: Cytokines as therapeutics and targets of therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Struyf S, Proost P, Van Damme J. Regulation of the immune response by the interaction of chemokines and proteases. Adv Immunol. 2003;81:1–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

