Protective effects of human iPS-derived retinal pigment epithelium cell transplantation in the retinal dystrophic rat
- PMID: 19997644
- PMCID: PMC2780911
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008152
Protective effects of human iPS-derived retinal pigment epithelium cell transplantation in the retinal dystrophic rat
Abstract
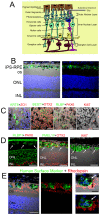
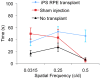
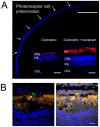
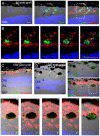
Transformation of somatic cells with a set of embryonic transcription factors produces cells with the pluripotent properties of embryonic stem cells (ESCs). These induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells have the potential to differentiate into any cell type, making them a potential source from which to produce cells as a therapeutic platform for the treatment of a wide range of diseases. In many forms of human retinal disease, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the underlying pathogenesis resides within the support cells of the retina, the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). As a monolayer of cells critical to photoreceptor function and survival, the RPE is an ideally accessible target for cellular therapy. Here we report the differentiation of human iPS cells into RPE. We found that differentiated iPS-RPE cells were morphologically similar to, and expressed numerous markers of developing and mature RPE cells. iPS-RPE are capable of phagocytosing photoreceptor material, in vitro and in vivo following transplantation into the Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) dystrophic rat. Our results demonstrate that iPS cells can be differentiated into functional iPS-RPE and that transplantation of these cells can facilitate the short-term maintenance of photoreceptors through phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments. Long-term visual function is maintained in this model of retinal disease even though the xenografted cells are eventually lost, suggesting a secondary protective host cellular response. These findings have identified an alternative source of replacement tissue for use in human retinal cellular therapies, and provide a new in vitro cellular model system in which to study RPE diseases affecting human patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
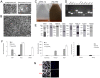
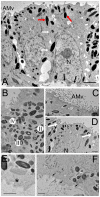
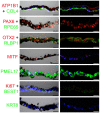
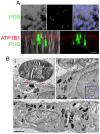
Similar articles
-
Generation of retinal pigment epithelial cells from small molecules and OCT4 reprogrammed human induced pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012 Feb;1(2):96-109. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2011-0057. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22532929 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Differentiation and Biological Characterization of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Curr Eye Res. 2020 Sep;45(9):1155-1167. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1722180. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31984806
-
Differentiation of RPE cells from integration-free iPS cells and their cell biological characterization.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Oct 2;8(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0652-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28969679 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium for an In Vitro Model of Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1186:33-53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-28471-8_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31654385 Review.
-
Stem cell based therapies for age-related macular degeneration: The promises and the challenges.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015 Sep;48:1-39. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 26113213 Review.
Cited by
-
Chapter 4 - Restoring Vision to the Blind: Stem Cells and Transplantation.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2014 Dec 30;3(7):6. doi: 10.1167/tvst.3.7.6. eCollection 2014 Dec. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2014. PMID: 25653890 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: Development in the Ophthalmologic Field.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2361763. doi: 10.1155/2016/2361763. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27594887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell therapy in retinal diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jul;18(7):1478-1485. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.361537. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36571345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative Regulators of Angiogenesis, Ocular Vascular Homeostasis, and Pathogenesis and Treatment of Exudative AMD.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2018 Oct-Dec;13(4):470-486. doi: 10.4103/jovr.jovr_67_18. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2018. PMID: 30479719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of ABCA4 in the retinal pigment epithelium and its implications for Stargardt macular degeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 20;115(47):E11120-E11127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1802519115. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30397118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- da Cruz L, Chen FK, Ahmado A, Greenwood J, Coffey P. RPE transplantation and its role in retinal disease. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2007;26:598–635. - PubMed
-
- Coffey PJ, Girman S, Wang SM, Hetherington L, Keegan DJ, et al. Long-term preservation of cortically dependent visual function in RCS rats by transplantation. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:53–56. - PubMed
-
- Tezel TH, Del Priore LV, Berger AS, Kaplan HJ. Adult retinal pigment epithelial transplantation in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143:584–595. - PubMed
-
- Gabrielian K, Oganesian A, Patel SC, Verp MS, Ernest JT. Cellular response in rabbit eyes after human fetal RPE cell transplantation. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1999;237:326–335. - PubMed
-
- Klimanskaya I, Hipp J, Rezai KA, West M, Atala A, et al. Derivation and comparative assessment of retinal pigment epithelium from human embryonic stem cells using transcriptomics. Cloning Stem Cells. 2004;6:217–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

