CS-SELEX generates high-affinity ssDNA aptamers as molecular probes for hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2
- PMID: 19997645
- PMCID: PMC2780912
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008142
CS-SELEX generates high-affinity ssDNA aptamers as molecular probes for hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2
Abstract
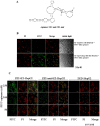
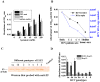
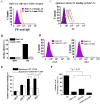
Currently, the development of effective diagnostic reagents as well as treatments against Hepatitis C virus (HCV) remains a high priority. In this study, we have described the development of an alive cell surface--Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (CS-SELEX) technique and screened the functional ssDNA aptamers that specifically bound to HCV envelope surface glycoprotein E2. Through 13 rounds of selection, the CS-SELEX generated high-affinity ssDNA aptamers, and the selected ssDNA aptamer ZE2 demonstrated the highest specificity and affinity to E2-positive cells. HCV particles could be specifically captured and diagnosed using the aptamer ZE2. A good correlation was observed in HCV patients between HCV E2 antigen-aptamer assay and assays for HCV RNA quantities or HCV antibody detection. Moreover, the selected aptamers, especially ZE2, could competitively inhibit E2 protein binding to CD81, an important HCV receptor, and significantly block HCV cell culture (HCVcc) infection of human hepatocytes (Huh7.5.1) in vitro. Our data demonstrate that the newly selected ssDNA aptamers, especially aptamer ZE2, hold great promise for developing new molecular probes, as an early diagnostic reagent for HCV surface antigen, or a therapeutic drug specifically for HCV.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
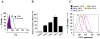

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection by DNA aptamer against envelope protein.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Oct;57(10):4937-44. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00897-13. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23877701 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Selection of High Affinity DNA and RNA Aptamers that Detect Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein of Genotypes 1 to 4 and Inhibit Virus Production in Cell Culture.J Mol Biol. 2022 Apr 15;434(7):167501. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167501. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35183559
-
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus production by aptamers against the core protein.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(4):1990-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03312-13. Epub 2013 Dec 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24307579 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Cell-Specific Aptamers: Recent Advances and Insight into the Selection Procedures.Molecules. 2017 Nov 27;22(12):2070. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122070. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29186905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SELEX Modifications and Bioanalytical Techniques for Aptamer-Target Binding Characterization.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2016 Nov;46(6):521-37. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2016.1157014. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2016. PMID: 26980177 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection by DNA aptamer against envelope protein.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Oct;57(10):4937-44. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00897-13. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23877701 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamers in diagnostics and treatment of viral infections.Viruses. 2015 Feb 16;7(2):751-80. doi: 10.3390/v7020751. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25690797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding of cellular nucleolin with the viral core RNA G-quadruplex structure suppresses HCV replication.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 10;47(1):56-68. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1177. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30462330 Free PMC article.
-
Broad-spectrum aptamer inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase closely mimic natural substrates.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Oct;39(18):8237-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr381. Epub 2011 Jul 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21727088 Free PMC article.
-
Selection and analytical applications of aptamers binding microbial pathogens.Trends Analyt Chem. 2011 Nov;30(10):1587-1597. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2011.08.006. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Trends Analyt Chem. 2011. PMID: 32287535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Memon MI, Memon MA. Hepatitis C: an epidemiological review. J Viral Hepatitis. 2002;9:84–100. - PubMed
-
- Gottwein JM, Bukh J. Cutting the Gordian knot-development and biological relevance of hepatitis C virus cell culture systems. Adv Virus Re. 2008;71:51–133. - PubMed
-
- Hsu CS, Liu CJ, Liu CH, Wang CC, Chen CL, et al. High hepatitis C viral load is associated with insulin resistance in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2008;28:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Smallwood GA, Devine R, Fasola C, Stieber AC, Heffron TG. Does interferon use prior to liver transplant influence hepatitis C outcomes following transplantation? Transplantation, 2008;86:1795–1798. - PubMed
-
- Liu CH, Liu CJ, Lin CL, Liang CC, Hsu SJ, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha-2a plus ribavirin for treatment-naive Asian patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:1260–1269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

