Haspin: a newly discovered regulator of mitotic chromosome behavior
- PMID: 19997740
- PMCID: PMC2839057
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-009-0250-4
Haspin: a newly discovered regulator of mitotic chromosome behavior
Abstract
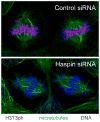
The haspins are divergent members of the eukaryotic protein kinase family that are conserved in many eukaryotic lineages including animals, fungi, and plants. Recently-solved crystal structures confirm that the kinase domain of human haspin has unusual structural features that stabilize a catalytically active conformation and create a distinctive substrate binding site. Haspin localizes predominantly to chromosomes and phosphorylates histone H3 at threonine-3 during mitosis, particularly at inner centromeres. This suggests that haspin directly regulates chromosome behavior by modifying histones, although it is likely that additional substrates will be identified in the future. Depletion of haspin by RNA interference in human cell lines causes premature loss of centromeric cohesin from chromosomes in mitosis and failure of metaphase chromosome alignment, leading to activation of the spindle assembly checkpoint and mitotic arrest. Haspin overexpression stabilizes chromosome arm cohesion. Haspin, therefore, appears to be required for protection of cohesion at mitotic centromeres. Saccharomyces cerevisiae homologues of haspin, Alk1 and Alk2, are also implicated in regulation of mitosis. In mammals, haspin is expressed at high levels in the testis, particularly in round spermatids, so it seems likely that haspin has an additional role in post-meiotic spermatogenesis. Haspin is currently the subject of a number of drug discovery efforts, and the future use of haspin inhibitors should provide new insight into the cellular functions of these kinases and help determine the utility of, for example, targeting haspin for cancer therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Bonenfant D, Towbin H, Coulot M, Schindler P, Mueller DR, van Oostrum J. Analysis of dynamic changes in post-translational modifications of human histones during cell cycle by mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6:1917–1932. - PubMed
-
- Caperta AD, Rosa M, Delgado M, Karimi R, Demidov D, Viegas W, Houben A. Distribution patterns of phosphorylated Thr 3 and Thr 32 of histone H3 in plant mitosis and meiosis. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;122:73–79. - PubMed
-
- Chignola F, Gaetani M, Rebane A, Org T, Mollica L, Zucchelli C, Spitaleri A, Mannella V, Peterson P, Musco G. The solution structure of the first PHD finger of autoimmune regulator in complex with non-modified histone H3 tail reveals the antagonistic role of H3R2 methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:2951–2961. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

