Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 19998274
- PMCID: PMC2946078
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23354
Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells
Erratum in
- Hepatology. 2010 Mar;51(3):1094
Abstract
There exists a worldwide shortage of donor livers available for orthotropic liver transplantation and hepatocyte transplantation therapies. In addition to their therapeutic potential, primary human hepatocytes facilitate the study of molecular and genetic aspects of human hepatic disease and development and provide a platform for drug toxicity screens and identification of novel pharmaceuticals with potential to treat a wide array of metabolic diseases. The demand for human hepatocytes, therefore, heavily outweighs their availability. As an alternative to using donor livers as a source of primary hepatocytes, we explored the possibility of generating patient-specific human hepatocytes from induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells.
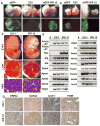
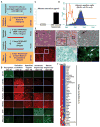
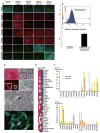
Conclusion: We demonstrate that mouse iPS cells retain full potential for fetal liver development and describe a procedure that facilitates the efficient generation of highly differentiated human hepatocyte-like cells from iPS cells that display key liver functions and can integrate into the hepatic parenchyma in vivo.
Figures

Comment in
-
Tumorigenicity of human induced pluripotent stem cells depends on the balance of gene expression between p21 and p53.Hepatology. 2010 Mar;51(3):1088-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.23396. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 19957368 No abstract available.
-
Hepatocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells: a giant leap forward for hepatology.Hepatology. 2010 Jan;51(1):20-2. doi: 10.1002/hep.23474. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20034034 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Park IH, Zhao R, West JA, et al. Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature. 2008;451:141–146. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
