Brain-behavior relationships in young traumatic brain injury patients: DTI metrics are highly correlated with postural control
- PMID: 19998364
- PMCID: PMC6870903
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20911
Brain-behavior relationships in young traumatic brain injury patients: DTI metrics are highly correlated with postural control
Abstract
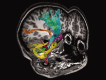
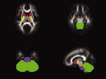
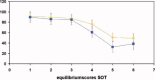
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of impairment and functional disability in children and adolescents, including deterioration in fine as well as gross motor skills. The aim of this study was to assess deficits in sensory organization and postural ability in a young group of TBI patients versus controls by using quantitative force-platform recordings, and to test whether balance deficits are related to variation in structural properties of the motor and sensory white matter pathways. Twelve patients with TBI and 14 controls (aged 8-20 years) performed the Sensory Organisation Test (SOT) protocol of the EquiTest (Neurocom). All participants were scanned using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) along with standard anatomical scans. Quantitative comparisons of DTI parameters (fractional anisotropy, axial and radial diffusivity) between TBI patients and controls were performed. Correlations between DTI parameters and SOT balance scores were determined. Findings revealed that the TBI group scored generally lower than the control group on the SOT, indicative of deficits in postural control. In the TBI group, reductions in fractional anisotropy were noted in the cerebellum, posterior thalamic radiation, and corticospinal tract. Degree of white matter deterioration was highly correlated with balance deficits. This study supports the view that DTI is a valuable tool for assessing the integrity of white matter structures and for selectively predicting functional motor deficits in TBI patients.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlations between white matter integrity and motor function in traumatic brain injury patients.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2011 Jul-Aug;25(6):492-502. doi: 10.1177/1545968310394870. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2011. PMID: 21427274
-
Training-induced improvements in postural control are accompanied by alterations in cerebellar white matter in brain injured patients.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Dec 17;7:240-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.12.006. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 25610786 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Detection of central white matter injury underlying vestibulopathy after mild traumatic brain injury.Radiology. 2014 Jul;272(1):224-32. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14132670. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Radiology. 2014. PMID: 24735411
-
Traumatic brain injury, major depression, and diffusion tensor imaging: making connections.Brain Res Rev. 2010 Sep;64(1):213-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 11. Brain Res Rev. 2010. PMID: 20388528 Review.
-
Relationship Between Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) Findings and Cognition Following Pediatric TBI: A Meta-Analytic Review.Dev Neuropsychol. 2016 Apr;41(3):176-200. doi: 10.1080/87565641.2016.1186167. Epub 2016 May 27. Dev Neuropsychol. 2016. PMID: 27232263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations between white matter integrity and postural control in adults with traumatic brain injury.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 27;18(11):e0288727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288727. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38011096 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal fixel-based analysis reveals restoration of white matter alterations following balance training in young brain-injured patients.Neuroimage Clin. 2021;30:102621. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102621. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Neuroimage Clin. 2021. PMID: 33780865 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptual Postural Imbalance and Visual Vertigo.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019 Mar 16;19(5):19. doi: 10.1007/s11910-019-0939-6. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30877392 Review.
-
White Matter Disruption in Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury: Results From ENIGMA Pediatric Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.Neurology. 2021 Jul 19;97(3):e298-e309. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012222. Neurology. 2021. PMID: 34050006 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of predictive MRI and functional biomarkers in a pediatric piglet traumatic brain injury model.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Feb;16(2):338-344. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.290915. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32859794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arfanakis K, Cordes D, Haughton VM, Carew JD, Meyerand ME ( 2002): Independent component analysis applied to diffusion tensor MRI. Magn Reson Med 47: 354–363. - PubMed
-
- Assaf Y, Pasternak O ( 2008): Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)‐based white matter mapping in brain research: a review. J Mol Neurosci 34: 51–61. Review. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C, Duda J, Aldroubi A ( 2000): In vivo fiber tractography using DT‐MRI data. Magn Reson Med 44: 625–632. - PubMed
-
- Benson RR, Meda SA, Vasudevan S, Kou Z, Govindarajan KA, Hanks RA, Millis SR, Makki M, Latif Z, Coplin W, Meythaler J, Haacke EM ( 2007): Global white matter analysis of diffusion tensor images is predictive of injury severity in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 24: 446–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

