Human umbilical cord blood cell therapy blocks the morphological change and recruitment of CD11b-expressing, isolectin-binding proinflammatory cells after middle cerebral artery occlusion
- PMID: 19998484
- PMCID: PMC2830323
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.22306
Human umbilical cord blood cell therapy blocks the morphological change and recruitment of CD11b-expressing, isolectin-binding proinflammatory cells after middle cerebral artery occlusion
Abstract
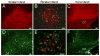
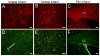
Secondary neurodegeneration resulting from stroke is mediated by delayed proinflammatory signaling and immune cell activation. Although it remains unknown which cell surface markers signify a proinflammatory phenotype, increased isolectin binding occurs on CD11b-expressing immune cells within injured brain tissue. Several reports have confirmed the efficacy of human umbilical cord blood (HUCB) cell therapy in reducing ischemic injury in rat after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), and these effects were attributed in part to dampened neuroinflammation. The present study examined the time course of lectin binding to cells of microglia/macrophage lineage within 96 hr after MCAO and whether delayed HUCB cell treatment alters the migration and/or morphological characteristics of these cells throughout the period of infarct expansion. Isolectin binding was up-regulated in response to injury, was maximal at 96 hr, and colocalized with cells that expressed the putative proinflammatory markers MMP-9 and nitric oxide. Isolectin-tagged fluorescence was also significantly increased at 72 hr and localized to greater numbers of amoeboid, CD11b-expressing cells relative to 51 hr. Treatment with 1 x 10(6) HUCB cells significantly reduced total lectin binding at 72 hr, as well as the total area occupied by lectin-tagged fluorescence at both 51 and 72 hr, relative to vehicle-treated controls. This effect was accompanied by a shift in the morphology of CD11b-positive cells from amoeboid to ramified shape. These data indicate that HUCB cell therapy suppressed the recruitment of proinflammatory, isolectin-binding cells during the period of infarct expansion, thus offering a potential mechanism for the protective effects of HUCB cell therapy.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Leukemia inhibitory factor modulates the peripheral immune response in a rat model of emergent large vessel occlusion.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Oct 15;15(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1326-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30322390 Free PMC article.
-
Monocytes are essential for the neuroprotective effect of human cord blood cells following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014 Mar;59:76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24472845 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord blood cells do not improve sensorimotor or cognitive outcome following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.Brain Res. 2006 Dec 6;1123(1):207-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.09.056. Epub 2006 Oct 30. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17070789
-
Human umbilical cord blood cells decrease microglial survival in vitro.Stem Cells Dev. 2010 Feb;19(2):221-8. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0170. Stem Cells Dev. 2010. PMID: 19788371 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated cerebral ischemic injury by activated macrophages/microglia after lipopolysaccharide microinjection into rat corpus callosum.Glia. 2005 Apr 15;50(2):168-81. doi: 10.1002/glia.20164. Glia. 2005. PMID: 15702482
Cited by
-
Histopathological Investigation of Different MCAO Modalities and Impact of Autologous Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cell Administration in an Ovine Stroke Model.Transl Stroke Res. 2011 Sep;2(3):279-93. doi: 10.1007/s12975-011-0101-5. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Transl Stroke Res. 2011. PMID: 23440305 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemia inhibitory factor modulates the peripheral immune response in a rat model of emergent large vessel occlusion.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Oct 15;15(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1326-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30322390 Free PMC article.
-
Implantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for ischemic stroke: perspectives and challenges.Front Med. 2015 Mar;9(1):20-9. doi: 10.1007/s11684-014-0371-x. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Front Med. 2015. PMID: 25491769 Review.
-
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Protects Neurons from Ischemic Damage via Upregulation of Superoxide Dismutase 3.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):608-622. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9587-2. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26746670 Free PMC article.
-
The spleen contributes to stroke induced neurodegeneration through interferon gamma signaling.Metab Brain Dis. 2012 Jun;27(2):131-41. doi: 10.1007/s11011-012-9283-0. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Metab Brain Dis. 2012. PMID: 22354752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajmo C, Jr, Vernon D, Collier L, Pennypacker K, Cuevas J. Sigma receptor activation reduces infarct size at 24 hours after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Cur Neurovascular Res. 2006;3(2):89–98. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Rothwell NJ. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2(10):734–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

