Value of three-dimensional reconstructions in pancreatic carcinoma using multidetector CT: initial results
- PMID: 19998504
- PMCID: PMC2791276
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.5827
Value of three-dimensional reconstructions in pancreatic carcinoma using multidetector CT: initial results
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the use of three-dimensional imaging of pancreatic carcinoma using multidetector computed tomography (CT) in a prospective study.
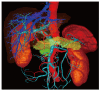
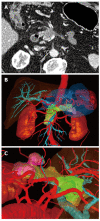
Methods: Ten patients with suspected pancreatic tumors were examined prospectively using multidetector CT (Somatom Sensation 16, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). The images were evaluated for the presence of a pancreatic carcinoma and invasion of the peripancreatic vessels and surrounding organs. Using the isotropic CT data sets, a three-dimensional image was created with automatic vascular analysis and semi-automatic segmentation of the organs and pancreatic tumor by a radiologist. The CT examinations and the three-dimensional images were presented to the surgeon directly before and during the patient's operation using the Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit-based software "ReLiver". Immediately after surgery, the value of the two images was judged by the surgeon. The operation and the histological results served as the gold standard.
Results: Nine patients had a pancreatic carcinoma (all pT3), and one patient had a serous cystadenoma. One tumor infiltrated the superior mesenteric vein. The infiltration was correctly evaluated. All carcinomas were resectable. In comparison to the CT image with axial and coronal reconstructions, the three-dimensional image was judged by the surgeons as better for operation planning and consistently described as useful.
Conclusion: A 3D-image of the pancreas represents an invaluable aid to the surgeon. However, the 3D-software must be further developed in order to be integrated into daily clinical routine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consistent surgeon evaluations of three-dimensional rendering of PET/CT scans of the abdomen of a patient with a ductal pancreatic mass.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 24;8(9):e75237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075237. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086475 Free PMC article.
-
A new invasion score for determining the resectability of pancreatic carcinomas with contrast-enhanced multidetector computed tomography.Pancreatology. 2008;8(2):204-10. doi: 10.1159/000128557. Epub 2008 Apr 23. Pancreatology. 2008. PMID: 18434758
-
Assessment of pancreatic tumor resectability with multidetector computed tomography: semiautomated console-generated images versus dedicated workstation-generated images.Acad Radiol. 2008 Aug;15(8):1058-68. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2008.03.005. Acad Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18620126
-
Cinematic rendering of pancreatic neoplasms: preliminary observations and opportunities.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018 Nov;43(11):3009-3015. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1559-3. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018. PMID: 29550959 Review.
-
[Computerized tomography of pancreatic tumors].Tumori. 1999 Jan-Feb;85(1 Suppl 1):S3-5. Tumori. 1999. PMID: 10235071 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Impact of the time interval between MDCT imaging and surgery on the accuracy of identifying metastatic disease in patients with pancreatic cancer.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Jan;204(1):W37-42. doi: 10.2214/AJR.13.12439. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015. PMID: 25539271 Free PMC article.
-
Improving prediction of surgical resectability over current staging guidelines in patients with pancreatic cancer who receive stereotactic body radiation therapy.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2018 Jul 19;3(4):601-610. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.07.002. eCollection 2018 Oct-Dec. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30370361 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Exosome-Derived microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Brazilian Pancreatic Cancer Patients.Biomolecules. 2022 May 31;12(6):769. doi: 10.3390/biom12060769. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740894 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, Preoperative Evaluation, and Assessment of Resectability of Pancreatic and Periampullary Cancer.Indian J Surg. 2015 Oct;77(5):362-70. doi: 10.1007/s12262-015-1370-0. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Indian J Surg. 2015. PMID: 26722198 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001846 facilitates the malignant behaviors of pancreatic cancer by sponging miR-204-3p and upregulating KRAS expression.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 11;9(1):448. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01733-2. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38081815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishiguchi T, Ota T, Naganawa S, Fukatsu H, Itoh S, Ishigaki T. CT and MR imaging of pancreatic cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001;48:923–927. - PubMed
-
- McNulty NJ, Francis IR, Platt JF, Cohan RH, Korobkin M, Gebremariam A. Multi--detector row helical CT of the pancreas: effect of contrast-enhanced multiphasic imaging on enhancement of the pancreas, peripancreatic vasculature, and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Radiology. 2001;220:97–102. - PubMed
-
- Prokesch RW, Chow LC, Beaulieu CF, Bammer R, Jeffrey RB Jr. Isoattenuating pancreatic adenocarcinoma at multi-detector row CT: secondary signs. Radiology. 2002;224:764–768. - PubMed
-
- Richter GM, Wunsch C, Schneider B, Düx M, Klar E, Seelos R, Kauffmann GW. [Hydro-CT in detection and staging of pancreatic carcinoma] Radiologe. 1998;38:279–286. - PubMed
-
- Schima W, Ba-Ssalamah A. [Radiologic staging of liver and pancreatic malignancies] Radiologe. 1999;39:568–577. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

