Iodized oil uptake assessment with cone-beam CT in chemoembolization of small hepatocellular carcinomas
- PMID: 19998505
- PMCID: PMC2791277
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.5833
Iodized oil uptake assessment with cone-beam CT in chemoembolization of small hepatocellular carcinomas
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the utility of assessing iodized oil uptake with cone-beam computed tomography (CT) in transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
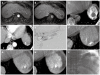
Methods: Cone-beam CT provided by a biplane flat-panel detector angiography suite was performed on eighteen patients (sixteen men and two women; 41-76 years; mean age, 58.9 years) directly after TACE for small HCC (26 nodules under 30 mm; mean diameter, 11.9 mm; range, 5-28 mm). The pre-procedural locations of the tumors were evaluated using triphasic multi-detector row helical computed tomography (MDCT). The tumor locations on MDCT and the iodized oil uptake by the tumors were analyzed on cone-beam CT and on spot image directly after the procedures.
Results: All lesions on preprocedural MDCT were detected using iodized oil uptake in the lesions on cone-beam CT (sensitivity 100%, 26/26). Spot image depicted iodized oil uptake in 22 of the lesions (sensitivity 85%). The degree of iodized oil uptake was overestimated (9%, 2/22) or underestimated (14%, 3/22) on spot image in five nodules compared with that of cone-beam CT.
Conclusion: Cone-beam CT is a useful and convenient tool for assessing the iodized oil uptake of small hepatic tumors (< 3 cm) directly after TACE.
Figures

References
-
- Murakami T, Kim T, Takamura M, Hori M, Takahashi S, Federle MP, Tsuda K, Osuga K, Kawata S, Nakamura H, et al. Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: detection with double arterial phase multi-detector row helical CT. Radiology. 2001;218:763–767. - PubMed
-
- Kim SK, Lim JH, Lee WJ, Kim SH, Choi D, Lee SJ, Lim HK, Kim H. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of dynamic three-phase computed tomography images and four-phase computed tomography images using multidetector row helical computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002;26:691–698. - PubMed
-
- Bartolozzi C, Lencioni R, Caramella D, Palla A, Bassi AM, Di Candio G. Small hepatocellular carcinoma. Detection with US, CT, MR imaging, DSA, and Lipiodol-CT. Acta Radiol. 1996;37:69–74. - PubMed
-
- De Santis M, Romagnoli R, Cristani A, Cioni G, Casolo A, Vici FF, Ventura E. MRI of small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with US, CT, DSA, and Lipiodol-CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1992;16:189–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

