Proteomic dissection of cell type-specific H2AX-interacting protein complex associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 20000738
- PMCID: PMC3670604
- DOI: 10.1021/pr900932y
Proteomic dissection of cell type-specific H2AX-interacting protein complex associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
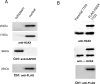
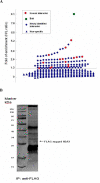
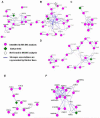
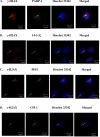
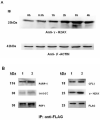
The replacement histone variant H2AX senses DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and recruits characteristic sets of proteins at its phosphorylated (gamma-H2AX) foci for concurrent DNA repair. We reasoned that the H2AX interaction network, or interactome, formed in the tumor-associated DNA DSB environment such as in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, where preneoplastic lesions frequently occur, is indicative of HCC pathogenic status. By using an in vivo dual-tagging quantitative proteomic method, we identified 102 H2AX-specific interacting partners in HCC cells that stably expressed FLAG-tagged H2AX at close to the endogenous level. Using bioinformatics tools for data-dependent network analysis, we further found binary relationships among these interactors in defined pathway modules, implicating H2AX in a multifunctional role of coordinating a variety of biological pathways involved in DNA damage recognition and DNA repair, apoptosis, nucleic acid metabolism, Ca(2+)-binding signaling, cell cycle, etc. Furthermore, our observations suggest that these pathways interconnect through key pathway components or H2AX interactors. The physiological accuracy of our quantitative proteomic approach in determining H2AX-specific interactors was evaluated by both coimmunoprecipitation/ immunoblotting and confocal colocalization experiments performed on HCC cells. Due to their involvement in diverse functions, the H2AX interactors involved in different pathway modules, such as Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1, 14-3-3 zeta, coflin 1, and peflin 1, were examined for their relative H2AX binding affinities in paired hepatocytes and HCC cells. Treatment with the DSB-inducing agent bleomycin enhanced binding of these proteins to H2AX, suggesting an active role of H2AX in coordinating the functional pathways of each protein in DNA damage recognition and repair.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reptin regulates DNA double strand breaks repair in human hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 15;10(4):e0123333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123333. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25875766 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic dissection of a native 14-3-3ε interacting protein complex associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.Amino Acids. 2014 Apr;46(4):841-52. doi: 10.1007/s00726-013-1644-4. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Amino Acids. 2014. PMID: 24363202
-
UBE2T-regulated H2AX monoubiquitination induces hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by facilitating CHK1 activation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 21;39(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01734-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33087136 Free PMC article.
-
[gamma H2AX in the recognition of DNA double-strand breaks].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009 Feb 27;63:92-8. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009. PMID: 19252467 Review. Polish.
-
Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Oct;36(17):5678-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn550. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18772227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA damage induces reactive oxygen species generation through the H2AX-Nox1/Rac1 pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Jan 12;3(1):e249. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.134. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22237206 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of DNA damage response pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:153867. doi: 10.1155/2014/153867. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24877058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pinacidil ameliorates cardiac microvascular ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting chaperone-mediated autophagy of calreticulin.Basic Res Cardiol. 2024 Feb;119(1):113-131. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-01028-8. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Basic Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38168863 Free PMC article.
-
H2AFX might be a prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Jan;6(1):e1684. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1684. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 35903980 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese superoxide dismutase interacts with a large scale of cellular and mitochondrial proteins in low-dose radiation-induced adaptive radioprotection.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Nov 15;53(10):1838-47. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.589. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 23000060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franco S, Alt FW, Manis JP. Pathways that suppress programmed DNA breaks from progressing to chromosomal breaks and translocations. DNA Repair (Amst) 2006;5(9–10):1030–41. - PubMed
-
- Phillips ER, McKinnon PJ. DNA double-strand break repair and development. Oncogene. 2007;26(56):7799–808. - PubMed
-
- Shrivastav M, De Haro LP, Nickoloff JA. Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Cell Res. 2008;18(1):134–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

