Na(+) and K(+) allosterically regulate cooperative DNA binding by the human progesterone receptor
- PMID: 20000807
- PMCID: PMC2808462
- DOI: 10.1021/bi901525m
Na(+) and K(+) allosterically regulate cooperative DNA binding by the human progesterone receptor
Abstract
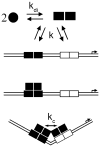
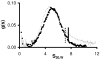
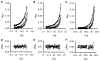
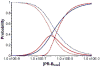
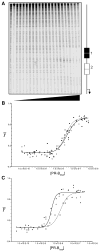
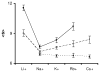
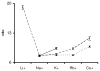
Cooperativity is a common mechanism used by transcription factors to generate highly responsive yet stable gene regulation. For the two isoforms of human progesterone receptor (PR-A and PR-B), differences in cooperative DNA binding energetics may account for their differing transcriptional activation properties. Here we report on the molecular origins responsible for cooperativity, finding that it can be activated or repressed with Na(+) and K(+), respectively. We demonstrate that PR self-association and DNA-dependent cooperativity are linked to a monovalent cation binding event and that this binding is coupled to modulation of receptor structure. K(+) and Na(+) are therefore allosteric effectors of PR function. Noting that the apparent binding affinities of Na(+) and K(+) are comparable to their intracellular concentrations and that PR isoforms directly regulate the genes of a number of ion pumps and channels, these results suggest that Na(+) and K(+) may additionally function as physiological regulators of PR action.
Figures

References
-
- Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. - PubMed
-
- Meyer ME, Quirin-Stricker C, Lerouge T, Bocquel MT, Gronemeyer H. A limiting factor mediates the differential activation of promoters by the human progesterone receptor isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10882–10887. - PubMed
-
- Sartorius CA, Melville MY, Hovland AR, Tung L, Takimoto GS, Horwitz KB. A third transactivation function (AF3) of human progesterone receptors located in the unique N-terminal segment of the B-isoform. Mol Endocrinol. 1994;8:1347–1360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

