Waterpipe tobacco smoking: an emerging health crisis in the United States
- PMID: 20001185
- PMCID: PMC3215592
- DOI: 10.5993/ajhb.34.3.3
Waterpipe tobacco smoking: an emerging health crisis in the United States
Abstract
Objective: To examine the prevalence and potential health risks of waterpipe tobacco smoking.
Methods: A literature review was performed to compile information relating to waterpipe tobacco smoking.
Results: Waterpipe tobacco smoking is increasing in prevalence worldwide; in the United States, 10-20% of some young adult populations are current waterpipe users. Depending on the toxicant measured, a single waterpipe session produces the equivalent of at least 1 and as many as 50 cigarettes. Misconceptions about waterpipe smoke content may lead users to underestimate health risks.
Conclusion: Inclusion of waterpipe tobacco smoking in tobacco control activities may help reduce its spread.
Figures
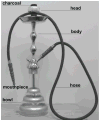
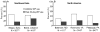
References
-
- World Health Organization. [Accessed August, 1, 2007];Factsheet No. 310: The top 10 causes of death. 2007 Available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/print.html.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Cigarette smoking among adults — United States, 2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56(44):1157–1161. - PubMed
-
- Knishknowy B, Amitai Y. Water-pipe (Narghile) smoking: an emerging health risk behavior. Pediatrics. 2005;116(1):e113–e119. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay A. Emperor Akbar as a healer and his eminent physicians. Bull Indian Inst Hist Med Hyderabad. 2000;30:151–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

