The NF-kappaB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy
- PMID: 20001209
- PMCID: PMC3043547
- DOI: 10.1517/14728220903431069
The NF-kappaB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy
Abstract
Importance of the field: Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) is activated by a variety of cancer-promoting agents. The reciprocal activation between NF-kappaB and inflammatory cytokines makes NF-kappaB important for inflammation-associated cancer development. Both the constitutive and anticancer therapeutic-induced NF-kappaB activation blunts the anticancer activities of the therapy. Elucidating the roles of NF-kappaB in cancer facilitates developing approaches for cancer prevention and therapy.
Areas covered in this review: By searching PubMed, we summarize the progress of studies on NF-kappaB in carcinogenesis and cancer cells' drug resistance in recent 10 years.
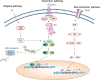
What the reader will gain: The mechanisms by which NF-kappaB activation pathways are activated; the roles and mechanisms of NF-kappaB in cell survival and proliferation, and in carcinogenesis and cancer cells' response to therapy; recent development of NF-kappaB-modulating means and their application in cancer prevention and therapy.
Take home message: NF-kappaB is involved in cancer development, modulating NF-kappaB activation pathways has important implications in cancer prevention and therapy. Due to the complexity of NF-kappaB roles in different cancers, careful evaluation of NF-kappaB's in each cancer type is crucial in this regard. More cancer cell-specific NF-kappaB inhibiting means are desired for improving anticancer efficacy and reducing systemic toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev. 2004;18(18):2195–224. - PubMed
-
- Devin A, Cook A, Lin Y, et al. The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity. 2000;12(4):419–29. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Lin Y, Guo Z, et al. The essential role of MEKK3 in TNF-induced NF-κB activation. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(7):620–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
