Systems biology of lupus: mapping the impact of genomic and environmental factors on gene expression signatures, cellular signaling, metabolic pathways, hormonal and cytokine imbalance, and selecting targets for treatment
- PMID: 20001421
- PMCID: PMC4020422
- DOI: 10.3109/08916930903374774
Systems biology of lupus: mapping the impact of genomic and environmental factors on gene expression signatures, cellular signaling, metabolic pathways, hormonal and cytokine imbalance, and selecting targets for treatment
Abstract
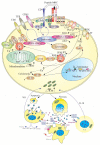
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is characterized by the dysfunction of T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells, the release of pro-inflammatory nuclear materials from necrotic cells, and the formation of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and immune complexes of ANA with DNA, RNA, and nuclear proteins. Activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) has recently emerged as a key factor in abnormal activation of T and B cells in SLE. In T cells, increased production of nitric oxide and mitochondrial hyperpolarization (MHP) were identified as metabolic checkpoints upstream of mTOR activation. mTOR controls the expression T-cell receptor-associated signaling proteins CD4 and CD3zeta through increased expression of the endosome recycling regulator Rab5 and HRES-1/Rab4 genes, enhances Ca2+ fluxing and skews the expression of tyrosine kinases both in T and B cells, and blocks the expression of Foxp3 and the generation of regulatory T cells. MHP, increased activity of mTOR, Rab GTPases, and Syk kinases, and enhanced Ca2+ flux have emerged as common T and B cell biomarkers and targets for treatment in SLE.
Figures

References
-
- Tenbrock K, Juang YT, Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC. Altered signal transduction in SLE T cells. Rheumatology. 2007;46(10):1525–1530. [Review] [78 refs] - PubMed
-
- Pascual V, Banchereau J, Palucka AK. The central role of dendritic cells and interferon-alpha in SLE. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15(5):548–556. [Review] [79 refs] - PubMed
-
- Crispin JC, Alcocer-Varela J. The role myeloid dendritic cells play in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev. 2007;6:450–456. [Review] [40 refs] - PubMed
-
- Kyttaris VC, Juang YT, Tsokos GC. Immune cells and cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: An update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17:518–522. [see comment]. [Review] [29 refs] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
