Immunologic and virologic events in early HIV infection predict subsequent rate of progression
- PMID: 20001854
- PMCID: PMC2939466
- DOI: 10.1086/649430
Immunologic and virologic events in early HIV infection predict subsequent rate of progression
Abstract
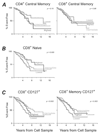
Background: Variability in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease progression cannot be fully predicted by CD4(+) T cell counts or viral load (VL). Because central memory T (T(CM)) cells play a critical role in the pathogenesis of simian immunodeficiency virus disease, we hypothesized that quantifying these cells in early HIV infection could provide prognostic information.
Methods: We measured expression of CD45RO, chemokine (C-C motif) receptor (CCR) 5, CCR7, CD27, and CD28 to enumerate naive and memory subsets in samples from recently infected individuals. We also quantified proliferation, CD127 expression, and cell-associated VL. Disease progression was compared across subgroups defined by these measurements, using Kaplan-Meier survival curves and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression.
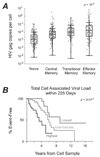
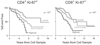
Results: Four hundred sixty-six subjects contributed 101 events. The proportion or absolute count of T(CM) cells did not correlate with disease progression, defined as the time to AIDS or death. However, significant associations were observed for proliferation within CD4(+) or CD8(+) T cells, loss of naive or CD127(+) memory CD8(+) T cells, and CD4(+) T cell-associated VL.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that the extent of the immunopathogenesis established early in HIV infection predicts the course of future disease. Because antiretroviral drug treatment reverses such defects in part, our study provides mechanistic clues to why early use of antiretrovirals may prove beneficial.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Giorgi JV, Ho HN, Hirji K, et al. CD8+ lymphocyte activation at human immunodeficiency virus type 1 seroconversion: development of HLA-DR+ CD38− CD8+ cells is associated with subsequent stable CD4+ cell levels The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:775–781. - PubMed
-
- Giorgi JV, Hultin LE, McKeating JA, et al. Shorter survival in advanced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection is more closely associated with T lymphocyte activation than with plasma virus burden or virus chemokine coreceptor usage. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:859–870. - PubMed
-
- Mellors JW, Rinaldo CR, Jr, Gupta P, White RM, Todd JA, Kingsley LA. Prognosis in HIV-1 infection predicted by the quantity of virus in plasma. Science. 1996;272:1167–1170. - PubMed
-
- El-Sadr WM, Lundgren JD, Neaton JD, et al. CD4+ count-guided interruption of antiretroviral treatment. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2283–2296. - PubMed
-
- Kitahata MGS, Moore R. Initiating rather than Deferring HAART at a CD4+ Count >500 Cells/mm3 Is Associated with Improved Survival. Presented at the 16th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 8 –11, 2009; Montreal, CA. 2009. Abstract number 71.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

