Post-transcriptional regulation of MEK-1 by polyamines through the RNA-binding protein HuR modulating intestinal epithelial apoptosis
- PMID: 20001965
- PMCID: PMC3021782
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20091459
Post-transcriptional regulation of MEK-1 by polyamines through the RNA-binding protein HuR modulating intestinal epithelial apoptosis
Abstract
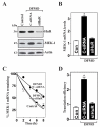
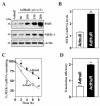
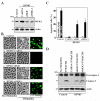
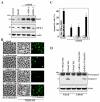
MEK-1 [MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) kinase-1] is an important signal transducing enzyme that is implicated in many aspects of cellular functions. In the present paper, we report that cellular polyamines regulate MEK-1 expression at the post-transcriptional level through the RNA-binding protein HuR (Hu-antigen R) in IECs (intestinal epithelial cells). Decreasing the levels of cellular polyamines by inhibiting ODC (ornithine decarboxylase) stabilized MEK-1 mRNA and promoted its translation through enhancement of the interaction between HuR and the 3'-untranslated region of MEK-1 mRNA, whereas increasing polyamine levels by ectopic ODC overexpression destabilized the MEK-1 transcript and repressed its translation by reducing the abundance of HuR-MEK-1 mRNA complex; neither intervention changed MEK-1 gene transcription via its promoter. HuR silencing rendered the MEK-1 mRNA unstable and inhibited its translation, thus preventing increases in MEK-1 mRNA and protein in polyamine-deficient cells. Conversely, HuR overexpression increased MEK-1 mRNA stability and promoted its translation. Inhibition of MEK-1 expression by MEK-1 silencing or HuR silencing prevented the increased resistance of polyamine-deficient cells to apoptosis. Moreover, HuR overexpression did not protect against apoptosis if MEK-1 expression was silenced. These results indicate that polyamines destabilize the MEK-1 mRNA and repress its translation by inhibiting the association between HuR and the MEK-1 transcript. Our findings indicate that MEK-1 is a key effector of the HuR-elicited anti-apoptotic programme in IECs.
Figures
References
-
- Radtke F, Clevers H. Self-renewal and cancer of the gut: two sides of a coin. Science. 2005;307:1904–1909. - PubMed
-
- Wang JY. Polyamines and mRNA stability in regulation of intestinal mucosal growth. Amino. Acids. 2005;33:241–252. - PubMed
-
- Orphanides G, Reinberg D. A unified theory of gene expression. Cell. 2002;108:439–451. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Liu L, Rao JN, Esmaili A, Strauch ED, Bass BL, Wang JY. JunD stabilization results in inhibition of normal intestinal epithelial cell growth through p21 after polyamine depletion. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:764–779. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Rao JN, Guo X, Liu L, Santora R, Bass BL, Wang JY. Polyamine depletion stabilizes p53 resulting in inhibition of normal intestinal epithelial cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2001;281:C941–C953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

